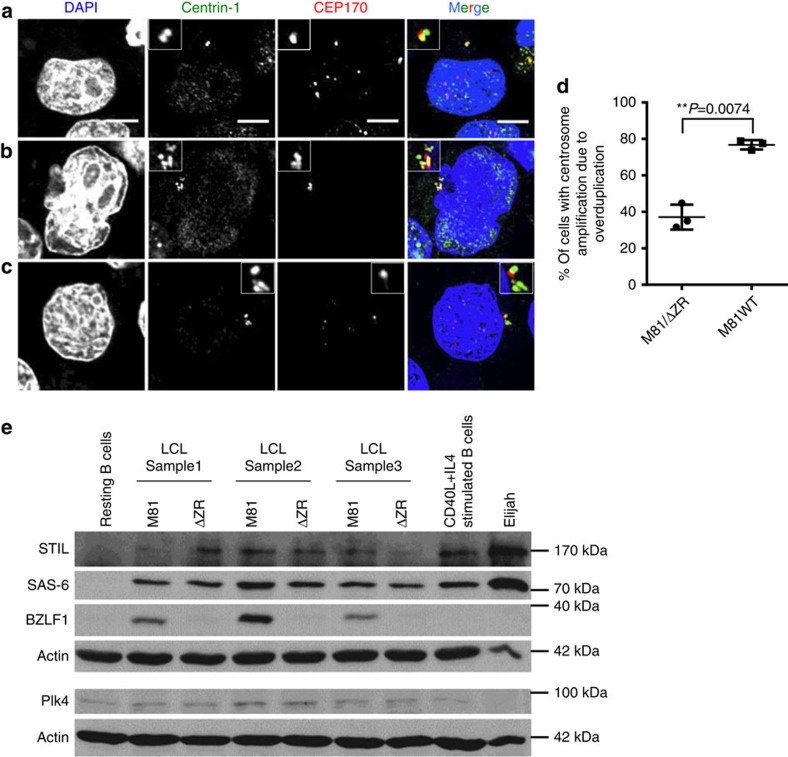
Figure 6. Centrosome amplification in wild-type EBV-infected cells mainly results from overduplication.
LCLs infected with wild-type virus were co-stained with antibodies specific to centrin-1 and CEP170, 2 proteins that localize to the centrosome, and counter-stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 5 μm. (a) This infected cell shows two centrin-positive centrioles (green) but only one centriole (red) expresses CEP170. (b) Infected bi-nucleated cell with centrosome accumulation showing staining for CEP170 in approximately 50% of the centrioles. (c) Infected cell showing centrosome overduplication with only one CEP170-positive centriole and at least four centrin-positive centrioles. (d) This graph shows the proportion of the cells with centrosome amplification that arose through overduplication in cells infected with wild-type M81 or with M81/ΔZR. The analysis was performed on three blood samples and the results were subjected to a paired two-tailed t-test (P=0.0074). Error bars represent the mean with s.d. (e) Immunoblots performed on three pairs of LCLs infected with either M81 or M81/ΔZR with antibodies specific to Plk4, Sas-6, STIL, actin or BZLF1. Non-infected resting B cells, B cells stimulated with CD40L and IL4, and the Burkitt's lymphoma cell line Elijah served as controls. We also included a western blot performed on U2OS, RPE-1 and HeLa cells with the same antibodies as controls in Supplementary Fig. 5. Please also see Supplementary Figs 11 and 12 for the uncropped full blots.