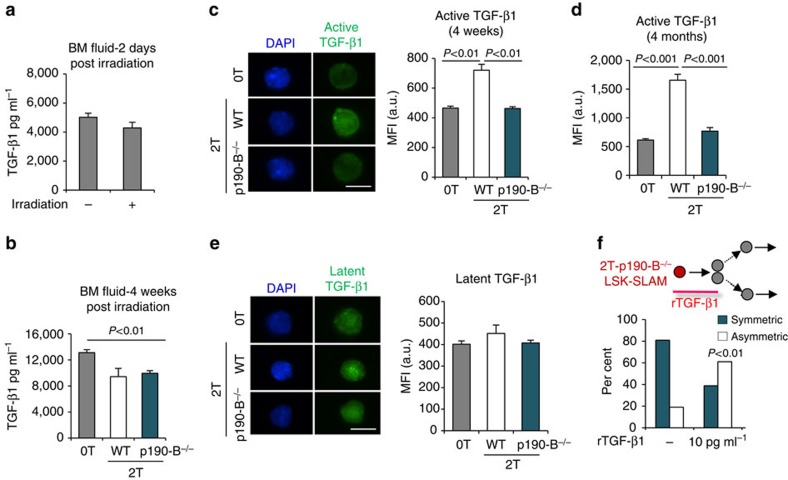
Figure 5. p190-B- deficiency prevents elevation of bioactive TGF-β in HSPCs.
(a,b) aTGF-β1 levels were measured by ELISA in BM fluid of control (0T) mice, and in recipient mice of WT cells 2 days following irradiation and transplantation (a) or in secondary recipient mice of WT and p190-B−/− cells 4 weeks following transplantation and in age matched control mice (b). Data are mean±s.e.m.; n=3 independent samples in each experiment, two-tailed unpaired t-test. (c,d) Detection of aTGF-β1 levels by immunofluorescence in LSK-SLAM 4 weeks (c) and 4 months (d) following transplantation. Representative images of LSK-SLAM isolated from control, 2T-WT and 2T-p190-B−/− mice (bioactive TGF-β1 (green) and DAPI (blue), scale bar 10 μm). Bar graph shows quantification of mean fluorescence intensity in each group (C&D are mean±s.e.m. from n=2 independent experiments, 35–50 cells from each experiment, two-tailed unpaired t-test). (e) Detection of latent TGF-β1 in LSK-SLAM 4 months following transplantation, by immunofluorescence (latent TGF-β1 (green) and DAPI (blue). Bar graph shows quantification of mean fluorescence intensity in each group (mean±s.e.m.; 35–50 cells from each experiment were analysed; n=2 experiments). (f) Effect of rTGF-β on 2T-p190-B−/− LSK-SLAM division output using the in vitro paired daughter cell assay as in Fig. 1. Single LSK-SLAM cells isolated from 2T-p190-B−/− recipients were treated with rTGF-β1 (10 pg ml−1) for one division; daughter cells were analysed as in Fig. 1. (n=17 pairs from two independent experiments, fisher exact 2 × 2 contingency table).