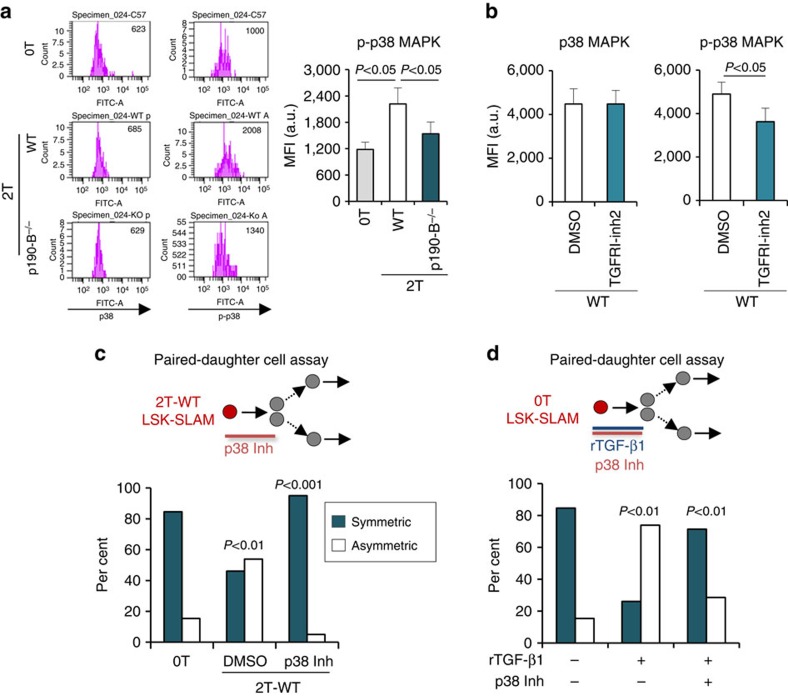
Figure 8. p38MAPK pathway mediates TGF-β effect on HSPC fate decisions.
(a) Flow cytometry analyses of p38MAPK and p-p38MAPK levels in LSK-SLAM from 0T, 2T WT and p190-B−/− mice (n=7 independent samples, from at least two independent experiments). (b) Flow cytometry analyses of p-p38MAPK levels in LSKCD48− cells from 2T-WT mice that were treated with TGF-β RI kinase inhibitor II or DMSO in vivo (n=9 independent samples from 2 independent experiments; mean±s.e.m., two-tailed unpaired t-test). (c) Effect of p38MAPK inhibitor on 2T-WT LSK-SLAM division output using the in vitro paired daughter cell assay as in Fig. 1. Single LSK-SLAM cells isolated from 2T-WT recipients were treated with p38MAPK inhibitor for one division; daughter cells were analysed as in Fig. 1. Bar graph shows per cent of symmetric and asymmetric divisions (n=20–26 pairs from three independent experiments). P values were calculated by Fisher exact 2 × 2 contingency table. (d) In vitro paired daughter cell assay performed with LSK-SLAM cells isolated from 0T mice and treated with rTGF-β1 alone or rTGF-β1+SB203580. Bar graph shows per cent of symmetric and asymmetric divisions (n=21–23 pairs in two independent experiments). P values were calculated by Fisher exact 2 × 2 contingency table.