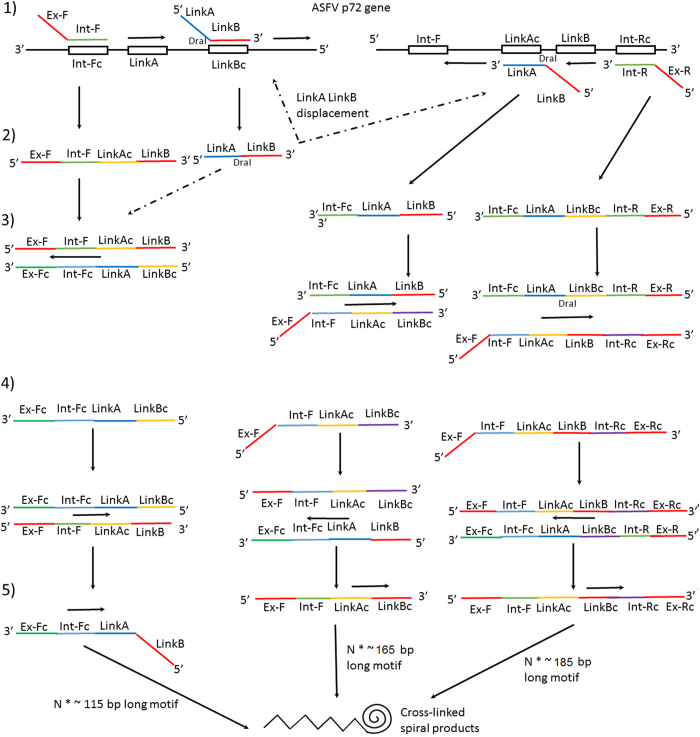
Figure 2. Mechanism of PCLSR.
At the initial stage the double structure of DNA is displaced by GspSSD polymerase (OptiGene, Horsham, West Sussex, United Kingdom). The first stage (1) on the left part shows the cross-linking primer is ligating with its LinkB fragment to the targeted sequence of p72 ASFV gene, then the polymerase extends the product from 5′ to the 3′ end of the structure. At the same time the process undergoes on the opposite 3′–5′ strand of p72 gene (right part). The outer primers ligate with their 3′ ends (Inf-F and Int-R) to the complementary external sequences of the targeted region. Amplification results in displacement of the newly synthesized products (left and right structure). Next, during the following stages the complementary strands are synthesized which leads to the target primary sequence multiplication. During the reaction progress three parallel structures with different sizes (115 bp, 165 bp and 185 bp) are synthesized (Structures 3, 4). The remaining 5′ ends of the products, namely ExF and ExR of outer-spiral primers which are reverse-complementary ligate to each other and form complex cross-linked spiral structures (Structure 5).