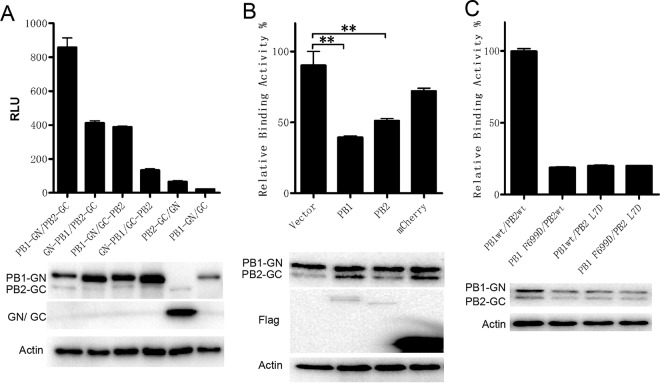
FIG 2.
The specificity and sensitivity of the BiLC assay were used to illustrate the PB1-PB2 interaction. (A) The interactions between influenza virus PB1 and PB2 were detected using the BiLC assay. PB2 and PB1 were fused to the N or C terminus of GC and GN, respectively. The interactions between the indicated pairs of fusion proteins were detected using the BiLC assay. The relative luminescence units (RLU) were determined by the use of a microplate reader. (B) Plasmids expressing PB1-GN and PB2-GC were cotransfected with empty vector or with vector expressing Flag-PB1, Flag-PB2, or Flag-mCherry. The RLU values of cell lysates were determined by the use of a microplate reader at 24 h posttransfection. The RLU value for samples containing vector was set to 100%. (C) The effects of site mutations on PB1 (F699D) or PB2 (L7D) on interactions between PB1 and PB2 were detected using the BiLC assay. The expression of proteins was detected by Western blotting as indicated. Data are shown as means ± SEM. **, P < 0.01 (Student's t test).