FIG 1.
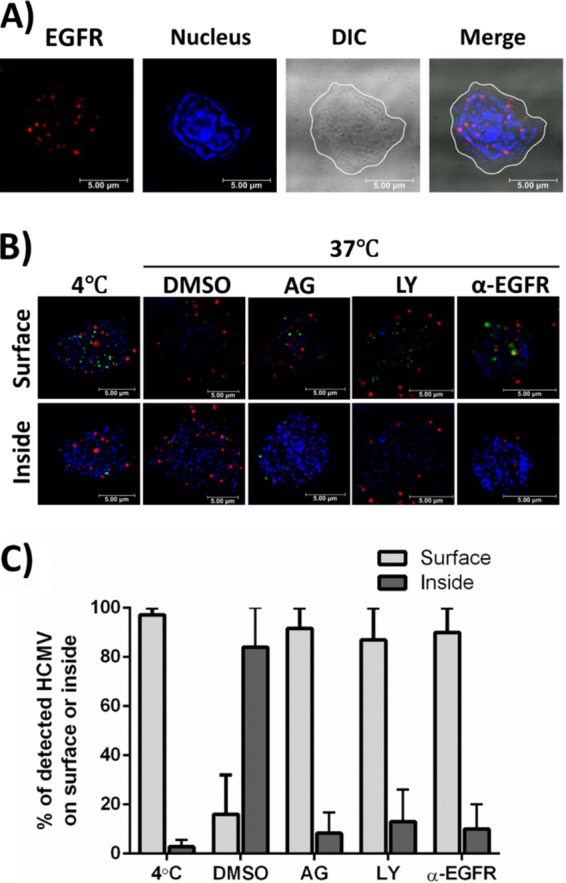
EGFR is expressed on the surfaces of CD34+ HPCs and is required for HCMV entry. (A) Uninfected CD34+ HPCs were stained with anti-EGFR antibodies and Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated secondary antibodies to detect EGFR expression on the cell surface (red). DAPI was used to counterstain the nucleus (blue). The contrast was adjusted in the differential interference contrast (DIC) image, and the cell membrane is outlined white in the DIC and merged images. Both adjustments were made so that the images could be more easily viewed. (B and C) Viral entry assays were performed in CD34+ HPCs. Cells were pretreated with AG1478 (AG) (EGFRK inhibitor), LY294002 (LY) (PI3K inhibitor), anti-EGFR blocking antibodies (α-EGFR), or DMSO/IgG antibody controls before HCMV infection. (B) Cells were infected with HCMV (TB40-UL32-HCMV/E) and stained with anti-EGFR antibodies and Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated secondary antibodies to detect EGFR (red). UL32-GFP was stained with an anti-GFP Alexa Flour 488-labeled antibody (green). DAPI was used to counterstain the nucleus (blue). Confocal microscopy was used to visualize HCMV bound to the cell surface or internalized into target cells. Representative slices from a Z stack are shown to compare the cell surface with intracellular space. (C) Quantification comparing the percentages of HCMV virions on the surfaces of or internalized into target cells. An average of 5 cells per experimental arm from two independent donors were used for counting. The means and standard errors of the mean (SEM) (error bars) of the results of two independent experiments performed.
