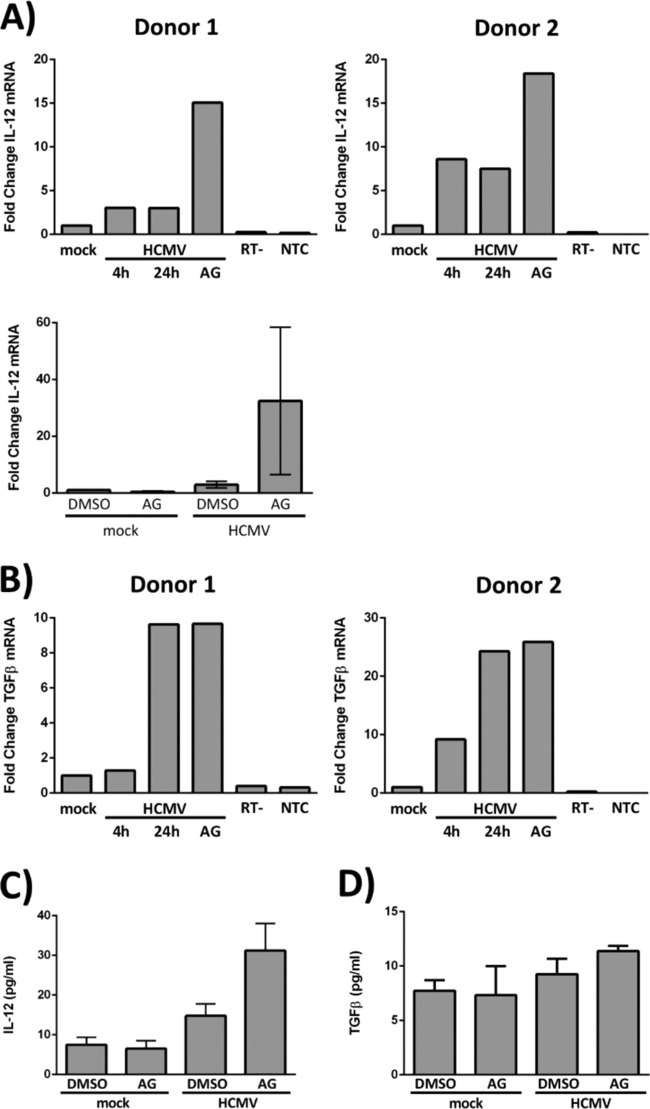
FIG 6.
HMCV infection alters the transcription of cellular hematopoietic factors, in part via EGFR signaling. (A and B) CD34+ HPCs were mock infected or HCMV infected for 4 h to allow viral entry and trafficking to the nucleus. (A, top row, and B) At 4 hpi, RNA was harvested from a single cohort of HCMV-infected cells to identify a baseline level of cellular transcripts in infected cells (4 h). DMSO or AG1478 (EGFRK inhibitor) was added to the other cohorts at 4 hpi, and RNA was isolated from the groups at 24 hpi (24 h and AG). (A, bottom) DMSO or AG1478 was added at 4 hpi, and RNA was isolated at 24 hpi. RT-qPCR was performed on all the samples to quantitate IL-12 (A) and TGF-β (B) transcripts. Expression levels for both IL-12 and TGF-β were normalized to 18S rRNA as an internal control; RT− and nontemplate controls are shown. (A, top row, and B) Fold changes in cellular transcripts examined in two different donors. (A, bottom) Averages from three independent experiments with different donors (the means and SEM [error bars] of the results of three independent experiments performed) are shown. (C and D) CD34+ HPCs were mock infected for 4 h before treatment with DMSO or AG1478. At 24 hpi, the supernatants were collected for quantification of IL-12 by ELISA (C) and TGF-β by multiplexed bead-based immunoassay (D). The graphs represent the average expression levels of IL-12 and TGF-β from three independent experiments with different donors. The means and SEM (error bars) of the results of three independent experiments performed are shown.