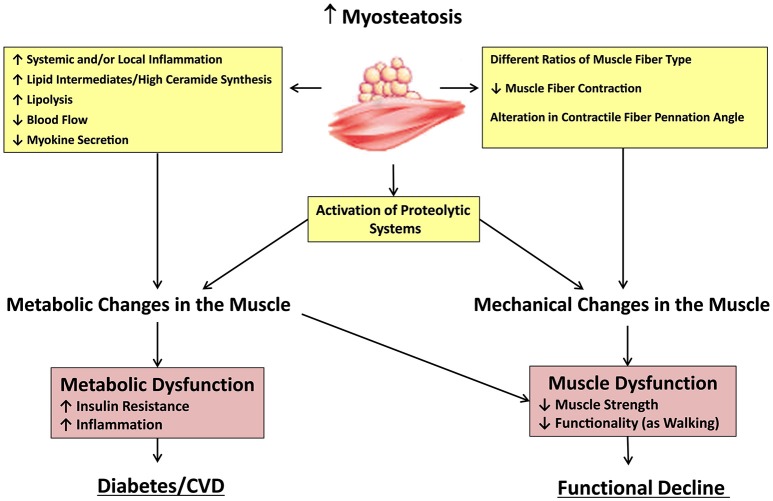
Figure 1.
Potential mechanisms underlying the effects of myosteatosis. Increased myosteatosis may lead to metabolic and mechanical changes in the muscle through a variety of mechanisms. Changes in muscle cell metabolism can lead to increased insulin resistance and inflammation, aiding in the development of diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Alterations in muscle architecture can also lead to muscular dysfunction and functional decline. Both processes may be increased through activation of proteolytic systems, which may also result from increased myosteatosis.