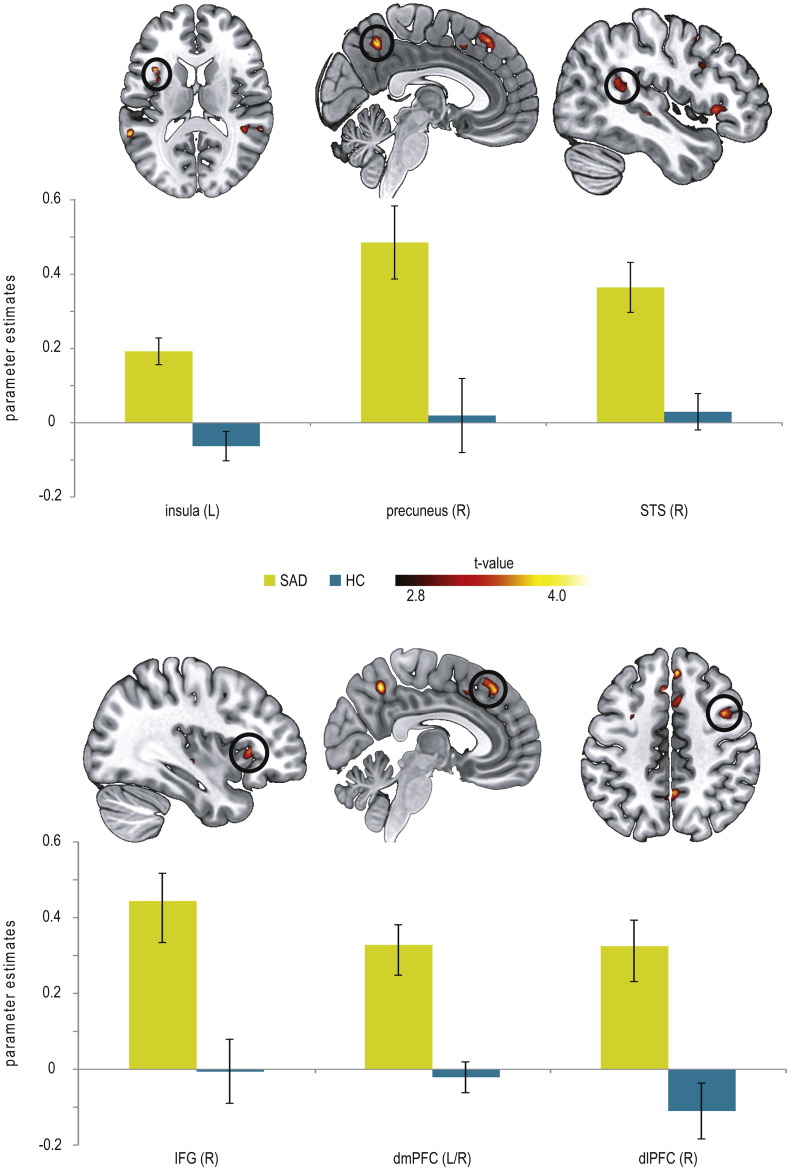
Fig. 3.
Differential brain activations during automatic disorder-related versus neutral scene processing in patients suffering from social anxiety disorder (SAD) as compared to healthy controls (HC) yielded by small-volume corrected analysis (P < 0.005 uncorrected, P < 0.05 corrected, L = left; R = right). SAD patients display enhanced activation in the insula (z = 14), precuneus (x = 4), superior temporal gyrus (STS; x = 46), inferior frontal gyrus (IFG; x = 36), dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC; x = 5), and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC; z = 46) compared with HC. Diagrams show contrasts of parameter estimates (disorder-related versus neutral; mean ± s.e.).