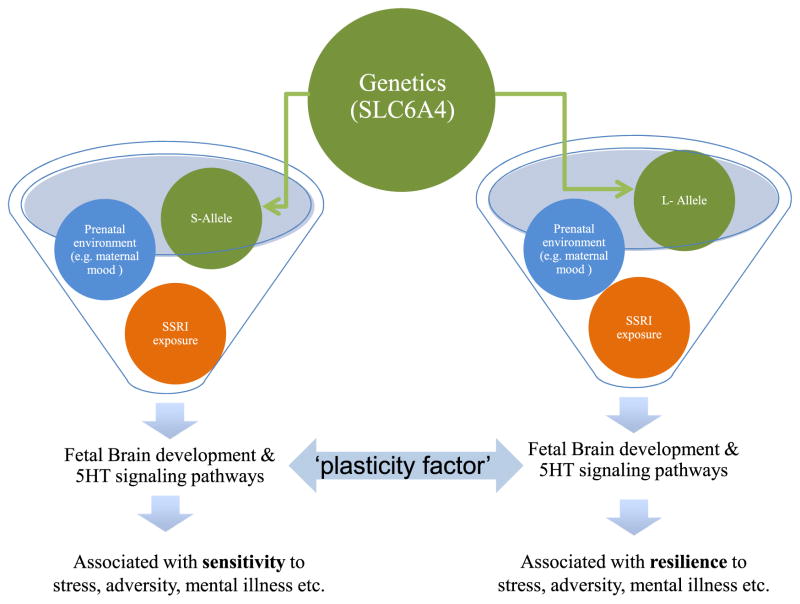
Fig. 1.
There is a complex interaction between genetic phenotype (s or l alleles for the SLC6A4 gene), in utero SSRI exposure, prenatal and postnatal environment to influence the 5-HT system. Depending on this interaction, certain conditions or environments can be protective or associated with an increased risk of mental illness later in life. Changes in central 5-HT levels during developmentally sensitive periods may act as ‘plasticity factors’ rather than ‘risk factors’ associated with vulnerability.