Fig 3.
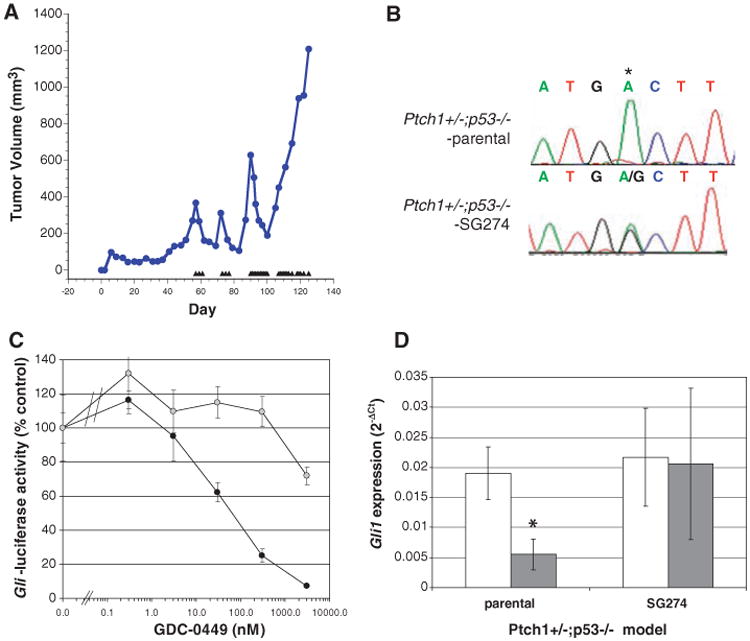
Acquired resistance to GDC-0449 through Smo mutation in a genetically engineered mouse model of medulloblastoma. (A) Medulloblastoma allografts from Ptch1+/−;p53−/− mice were made GDC-0449–resistant through intermittent daily dosing with 75 mg/kg GDC-0449. Treatment days are represented by triangles, and tumors were excised once they failed to respond to twice-daily dosing with GDC-0449. (B) Nucleotide sequence tracings from parental and a GDC-0449–resistant (SG274) medulloblastoma allografts showing a heterozygous mutation resulting in a D>G change at amino acid 477 of Smo (homologous to position 473 of human SMO). (C) GLI-luciferase reporter activity in C3H10T1/2 cells transfected with SMO-WT (closed circles) or SMO-D473G (open circles) after treatment with various doses of GDC-0449. (D) Quantitation of Gli1 mRNA levels by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction from multiple (n = 3) tumors collected 6 hours after treatment with vehicle control (open bars) or 75 mg/kg GDC-0449 (closed bars) from parental and SG274 tumor-bearing mice. Data indicate mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 (t test).
