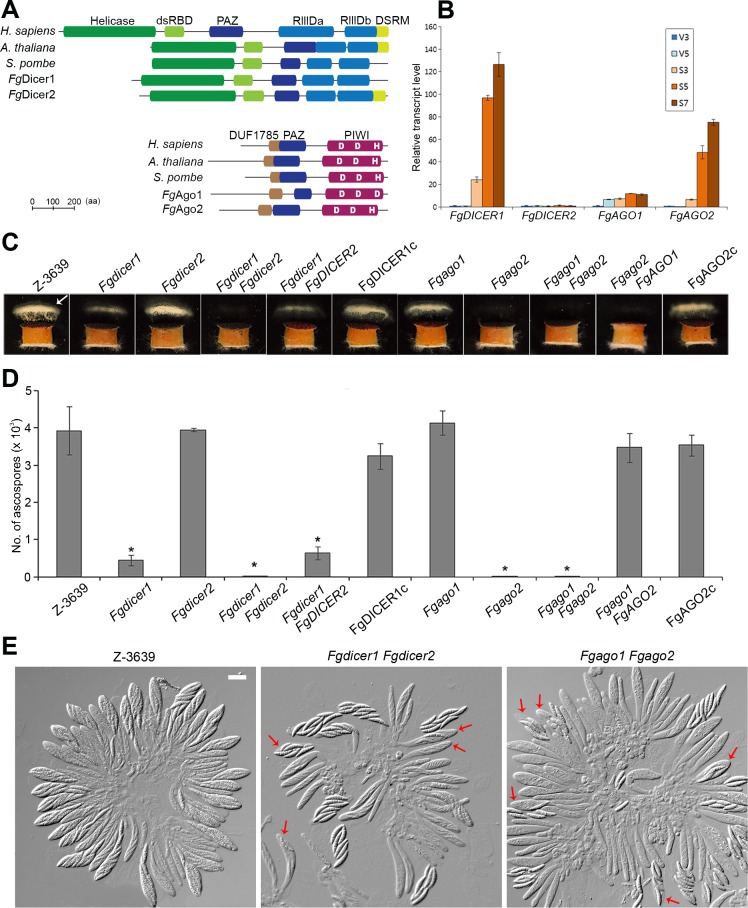
Fig 1. Characterization of Dicers and Argonautes in F. graminearum.
(A) Domain architectures of F. graminearum Dicer and Argonaute proteins along with those of representative orthologs. Domains were predicted using SMART [38]. Conservation analysis of the Asp-Asp-His (DDH) motif that comprises the active sites of Argonautes. The DDH motif is conserved in FgAgo2, but the third histidine residue is replaced by an aspartate in FgAgo1. The amino acid sequences of orthologs: Homo sapiens Dicer1 (NP_803187), Arabidopsis thaliana Dcl2 (NP_566199), Schizosaccharomyces pombe Dcl1 (Q09884), F. graminearum FgDicer1 (Gene ID: FGSG_09025), FgDicer2 (Gene ID: FGSG_04408), H. sapiens Ago2 (NP_036286), A. thaliana Ago1 (NP_849784), S. pombe Ago1 (NP_587782), F. graminearum FgAgo1 (Gene ID: FGSG_16976), and F. graminearum FgAgo2 (Gene ID: FGSG_00348). (B) Expression profiles of FgDICER1, FgDICER2, FgAGO1, and FgAGO2 in the F. graminearum wild-type strain during vegetative and sexual development. Transcript levels were analyzed via qRT-PCR during the vegetative (V3 and V5, 3 and 5 days after inoculation, respectively) and sexual stages (S3, S5 and S7, 3, 5, and 7 days after sexual induction, respectively) on carrot agar. The transcript level of the gene at the 3-day vegetative stage (V3) was arbitrarily set to 1, and this value was used for comparison to other periods. (C) Forcible ascospore discharge. A semi-circular agar block covered with perithecia was placed on a coverslip. Images were collected 48 h after the assay was initiated. White cloudy material (indicated with an arrow) represents discharged ascospores. (D) Number of discharged ascospores. Discharged ascospores were corrected for one week from the 7-day-old sexually induced cultures. (E) Asci rosettes. Imaging was performed 8 days after sexual induction. Red arrows indicate asci with defective ascospore delimitation. Scale bar = 20 μm.