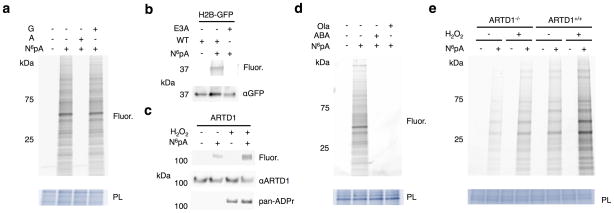
Figure 2.
N6pA labels ADP-ribosylated proteins in mammalian cells. a) HeLa cells were labeled with 1 mM N6pA ± 5 mM adenosine (A) or 5 mM guanosine (G) for 1 h. Cell lysates were then reacted with az-rho and analyzed by in-gel fluorescence profiling. PL = protein loading control. Fluor = fluorescence. b) HEK293T cells were transfected with H2B-GFP or the GLu3Ala ADP-ribosylation mutant, labeled 1 mM N6pA for 1 h, followed by immunopurification for GFP, and reacted with az-Rho. c) N6pA labels endogenous ARTD1 from HEK293T cells under oxidative stress. HEK293T cells were labeled 50 μM N6pA for 8 h and treated with 4 mM H2O2 for 1 h followed immunopurification for ARTD1. d) N6pA labeling of proteins is blocked by ARTD inhibitors: HeLa cells were labeled with 1 mM N6pA for 1 h and pretreated with either 10 μM olaparib (Ola) or 20 mM 3-aminobenzamide (ABA) 1 h before N6pA labeling and reacted with az-Rho. e) Wild type and ARTD1−/− MEFs were labeled with 50 μM N6pA for 8h and then treated with 4 mM H2O2 for 1 h. The cell lysates were then reacted with az-Rho. Full gels are located in Supplementary figure 2.