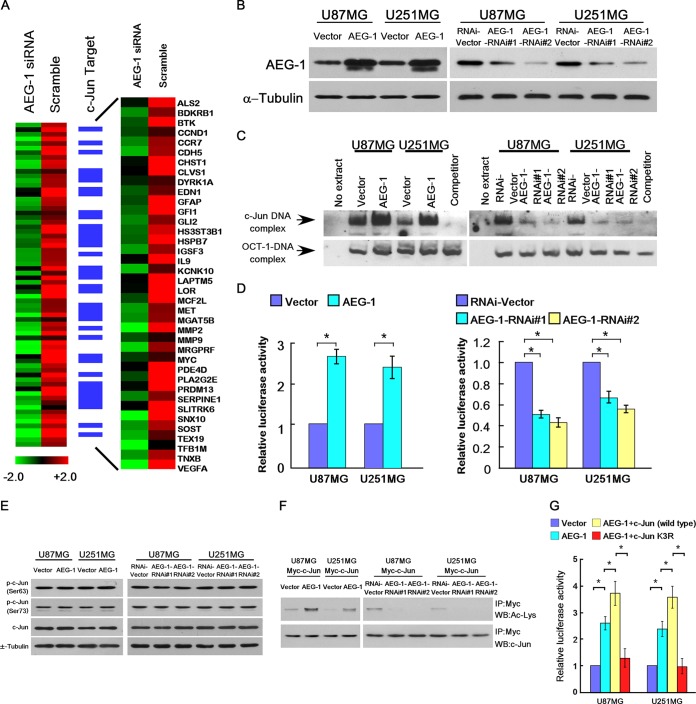
FIG 1.
AEG-1 promotes c-Jun transactivation via acetylation. (A) Expression profile of U87MG cells transfected with AEG-1-specific siRNA or the scrambled siRNA control. (B) Ectopic expression of AEG-1 and knockdown of AEG-1 expression in the U87MG and U251MG glioma cell lines were analyzed by immunoblotting using an anti-AEG-1 antibody. α-Tubulin was utilized as the loading control. (C) Changes in the DNA-binding affinity of c-Jun in the indicated cells on the basis of the results of EMSA analysis. (D) Induction of c-Jun activity by AEG-1 overexpression and repression of c-Jun activity by AEG-1-RNAi in U87MG and U251MG glioma cells, as demonstrated using a luciferase activity assay. (E) Western blotting of levels of phosphorylated c-Jun (p-c-Jun) with phosphorylation at Ser63, phosphorylated c-Jun with phosphorylation at Ser73, and total c-Jun were examined in AEG-1-overexpressing or -knockdown cells. α-Tubulin was detected as a loading control. IP, immunoprecipitation. (F) Western blot analysis of acetylated c-Jun expression in the indicated cells. Ac, acetylated. (G) Changes in c-Jun activity in the indicated AEG-1-transfected cells transfected with wild-type c-Jun or the K3R-c-Jun mutant expression construct. The bars represent the mean values ± SDs obtained from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05, Student's t test.