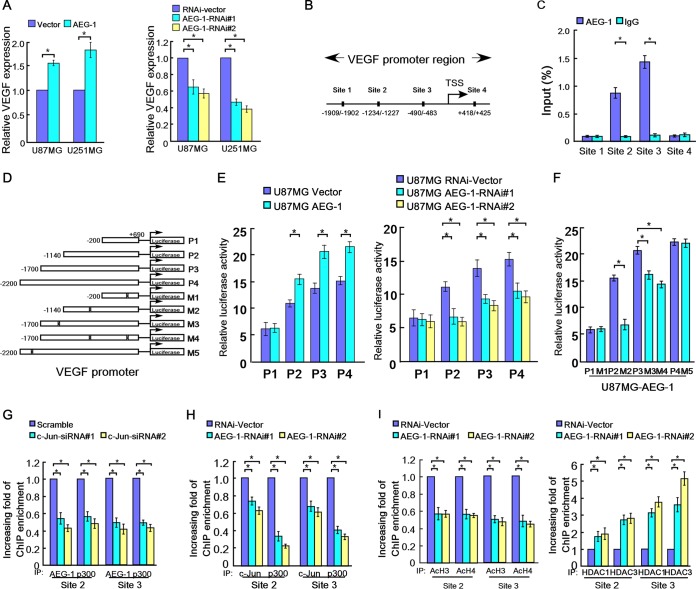
FIG 3.
AEG-1 establishes an acetylated chromatin state that favors transcriptional activation. (A) Levels of VEGF secretion by the indicated cells, as determined by ELISA. (B) Schematic illustration showing four deduced c-Jun-binding sites within the VEGF promoter. TSS, transcription start site. (C) ChIP assay results showing AEG-1 enrichment at the second and third c-Jun-binding sites within the VEGF promoter. (D) Schematic illustration of the truncated VEGF promoter constructs and the constructs with mutated c-Jun-binding sites. (E) Levels of transactivating activity of serial VEGF promoter fragments in the indicated U87MG cells. (F) Levels of transactivation activity of serial VEGF promoter fragments and the corresponding fragments with mutant c-Jun-binding sites in U87MG cells overexpressing AEG-1. (G) Levels of enrichment of AEG-1 and p300 on the AEG-1-bound c-Jun-binding sites in the indicated cells, determined by ChIP assay. (H) Levels of enrichment of c-Jun and p300 on AEG-1-bound c-Jun-binding sites in the indicated cells, determined by ChIP assay. (I) Levels of enrichment of acetylated histones H3 and H4, HDAC1, and HDAC3 at AEG-1-bound c-Jun-binding sites in the indicated cells, determined by ChIP assay. The bars represent the mean values ± SDs obtained from three independent experiments.*, P < 0.05, Student's t test.