FIG 3.
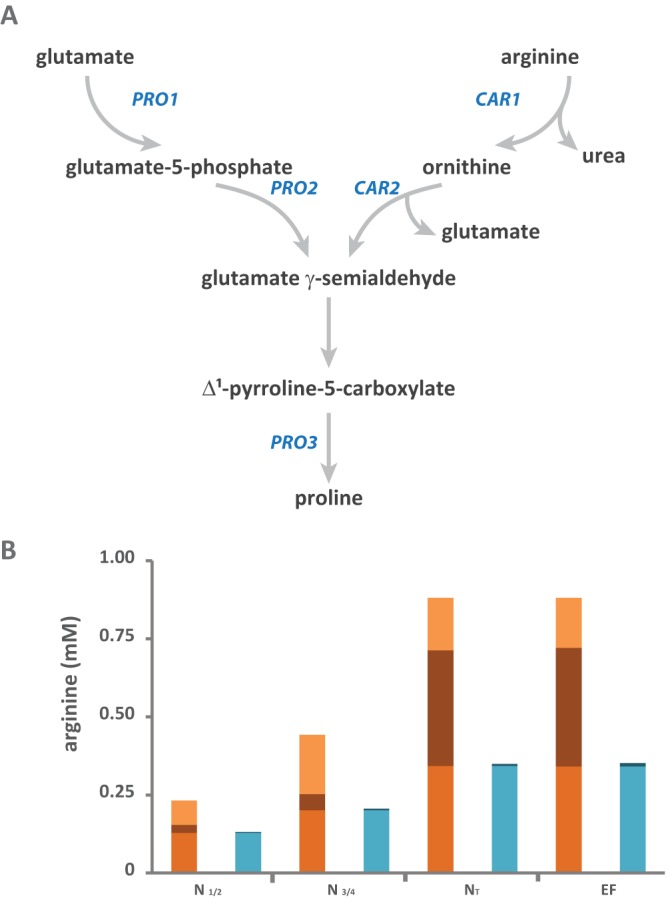
Focus on the fate of arginine during fermentation. (A) Schematic representation of the connections between the metabolic pathways involved in proline biosynthesis and those involved in arginine and glutamate degradation. (B) Isotopic labeling from 15N-labeled arginine during fermentation. Consumed arginine (orange) was mainly incorporated directly into proteins (medium orange) and was used to provide nitrogen for the de novo synthesis of other amino acids (brown) (calculated from the biomass content in proteinogenic amino acids and their isotopic enrichments). The labeled fraction of proteinogenic arginine (light blue) represents the consumed arginine directly incorporated into proteins, while the unlabeled fraction (dark blue) corresponds to de novo-synthesized arginine. The raw data and details of the calculations are provided in the supplemental material. N½, partial (one-half) nitrogen consumption; N¾, partial (three-fourths) nitrogen consumption; NT, complete nitrogen consumption; EF, end of fermentation.
