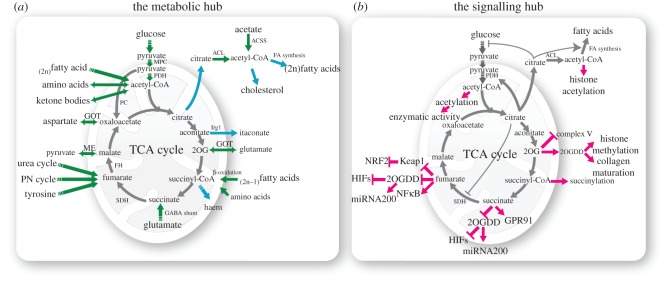
Figure 1.
The metabolic and signalling roles of TCA cycle metabolites. (a) In this panel, the major sources (green arrows) and fates (blue arrows) of TCA cycle metabolites are indicated. Dotted arrows indicate multi-step reactions, whereas solid lines indicate a single-step reaction. (b) Mitochondrial metabolites are also key signalling molecules. Some of the most established signalling functions of TCA cycle metabolites are indicated (purple arrows). ACL, ATP-citrate lyase; ACSS, acetyl-CoA synthetase; FA, fatty acid; FH, fumarate hydratase; GABA, gamma amino butyric acid; GOT, glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase; GPR91, G-protein-coupled receptor 91, also known as succinate receptor; Irg1, immunoresponsive 1 homologue, also known as aconitate dehydrogenase; ME, malic enzyme; MPC, mitochondrial pyruvate carrier; 2OGDH, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase; 2OGDD, 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases; PC, pyruvate carboxylase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; PN, purine nucleotides; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase.