Figure 1. Representative fundus photographs of posterior pole and optical coherence tomography (OCT) images of the fovea in eyes with optic nerve hypoplasia (ONH) and control eyes.
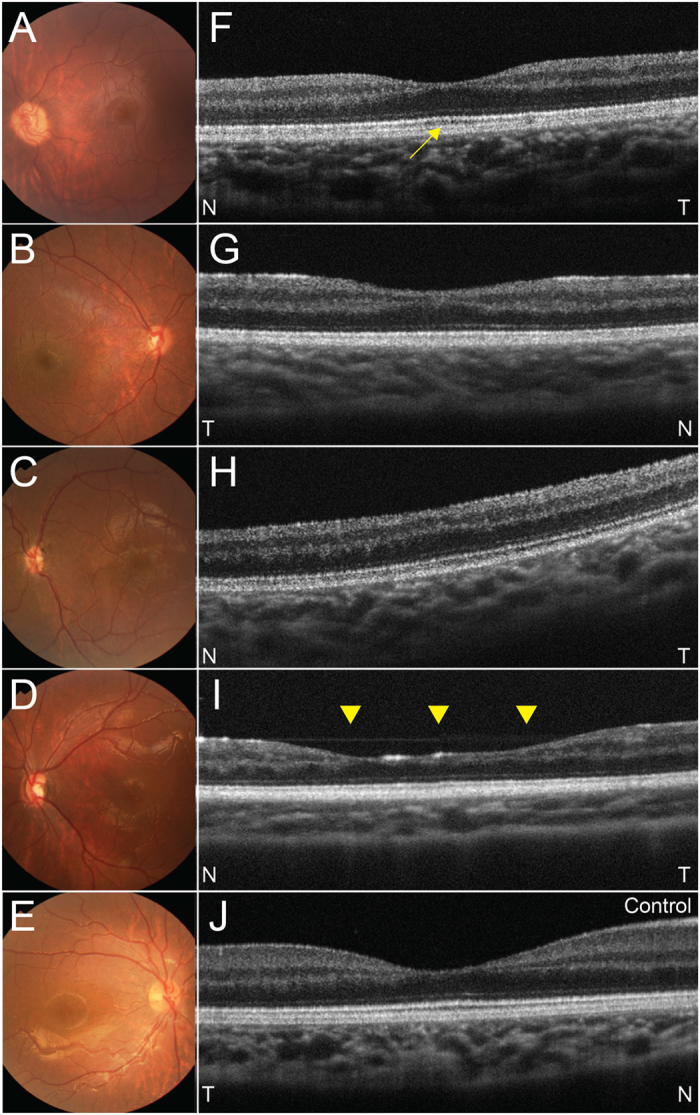
(A–D) Fundus photographs in eyes with ONH. Fundus photographs show that the optic disc sizes are small in all four eyes with under 0.30 of the ratio of horizontal disc diameter to the disc-macula distance. A yellowish peripapillary halo also exists in all four eye. (E) fundus photograph of a control right eye. (F–I) OCT images in eyes with ONH. Each image corresponds to fovea in (A–D) respectively. (F) A left eye with a subnormal fovea. The foveal depression is normal but seems to be shallow due to thinning of the ganglion cell complex. Outer segment lengthening is seen (yellow arrow). (G) A right eye with foveal hypoplasia. The foveal depression is incomplete and no outer segment lengthening is apparent. (H) A left eye with foveal hypoplasia. No foveal depression or outer segment lengthening is seen. Outer nuclear layer widening is seen. (I) A left eye with an atypical foveal abnormality. A foveal depression exists but is wide compared with other types (yellow arrow heads). (J) OCT image of a control right eye. T = temporal, N = nasal.
