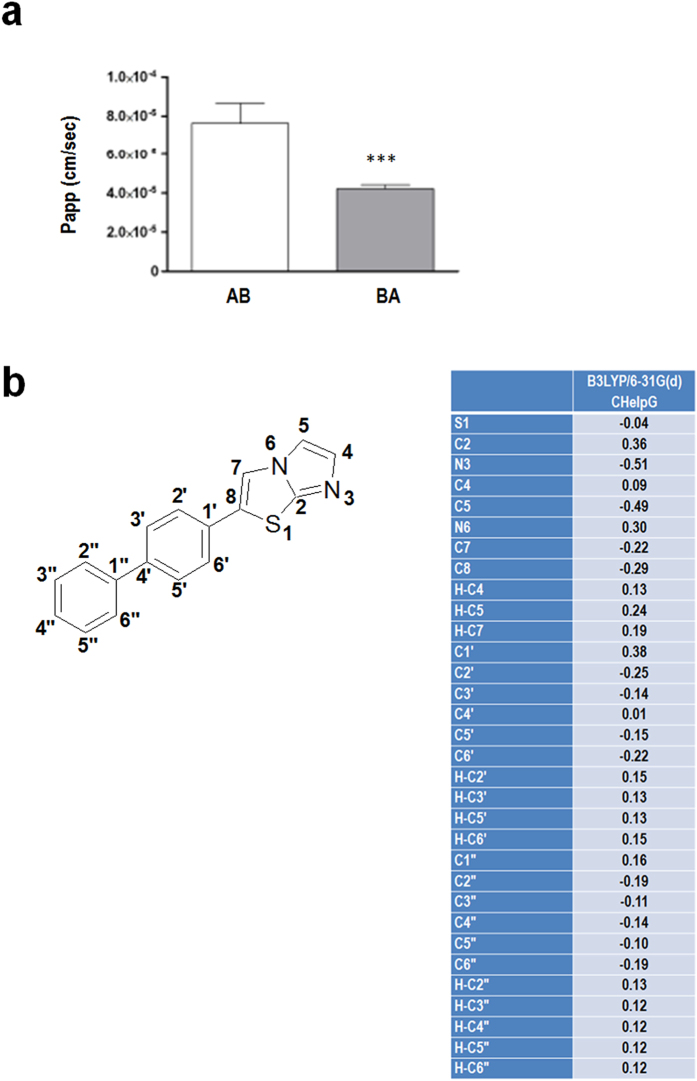
Figure 3. AUTEN-99 effectively crosses a blood-brain barrier culture model.
(a) Permeability of AUTEN-99 across a blood-brain model in AB (from blood to brain) and BA (from brain to blood) directions (n = 3). Papp [apparent permeability coefficient (given in 10−5 cm/s)] shows the speed of penetration of a given material across a barrier. Permeability coefficient of AUTEN-99 is particularly high in AB direction, indicating a fast penetration across the cell layers of the model. The amount of AUTEN-99 which crossed the barrier model in AB direction was 36.24% of the total added material, while it was 13.23% in BA direction. Both values represent a very significant penetration of the molecule. Bars represent mean ± S.D., ***p < 0.001, two-sample Student’s t-test. (b) Quantum chemical calculations of AUTEN-99. Left panel: the numbering scheme of AUTEN-99. Right panel: the calculated partial charges of atoms in AUTEN-99. Significantly negative partial charge is assigned to the N3 nitrogen and its lone electron pair. Therefore, it can be protonated and is a possible hydrogen bond acceptor site. Charge distribution on carbons of the biphenyl moiety is balanced and symmetrical, which provides the molecule with high level of lipophilicity, and poor water-solubility, especially in basic media. Its lipophilicity in terms of logP value was also calculated, using the SYBYL software package (see the Materials and Methods), and it has been found to be 3.85 (with the treatment of all hydrogens, polar proximity via bond), a high level of lipophilicity.