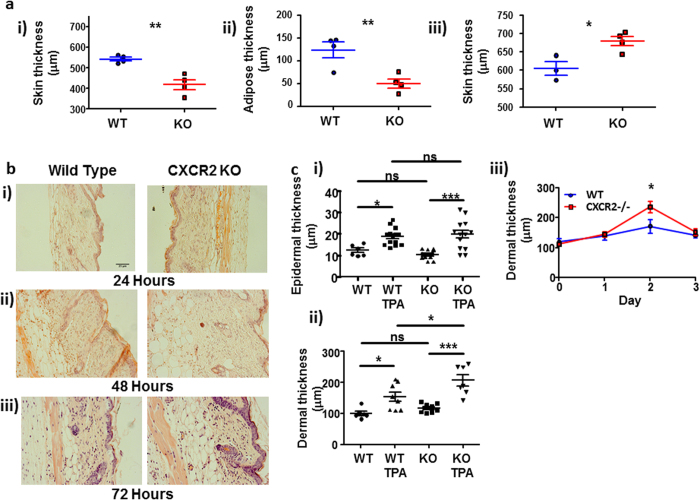
Figure 1. CXCR2-deficient mice display excessive cutaneous inflammatory responses.
(a) The dorsal skin thickness of (i) resting or (iii) TPA treated (48 hours) wild type or CXCR2-deficient mice was measured using callipers and the adipose layer thickness (ii) of resting skin was digitally measured by microscopy on haematoxylin and eosin stained skin sections. (b) Dorsal skin from WT and CXCR2-deficient mice treated with TPA for (i) 24, (ii) 48 or (iii) 72 hours were sectioned and stained with haematoxylin and eosin and imaged using light microscopy. (c) Stained sections from skin harvested 48 hours after vehicle or TPA treatment were analysed to measure (i) epidermal and (ii) dermal thickness. (iii) dermal thickness is also shown from sections harvested over the post-TPA application period. a and ciii: Data are plotted as the mean (±SEM) of one experiment undertaken with 3–6 individual mice, representative of at least two independent experiments *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 as determined using Students T test. Ci and Cii: Data plotted as the mean (± SEM) of two experiments each undertaken in 4–7 mice *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 as determined using repeated measures ANOVA analysis with Tukey’s post hoc test.