Fig. 3.
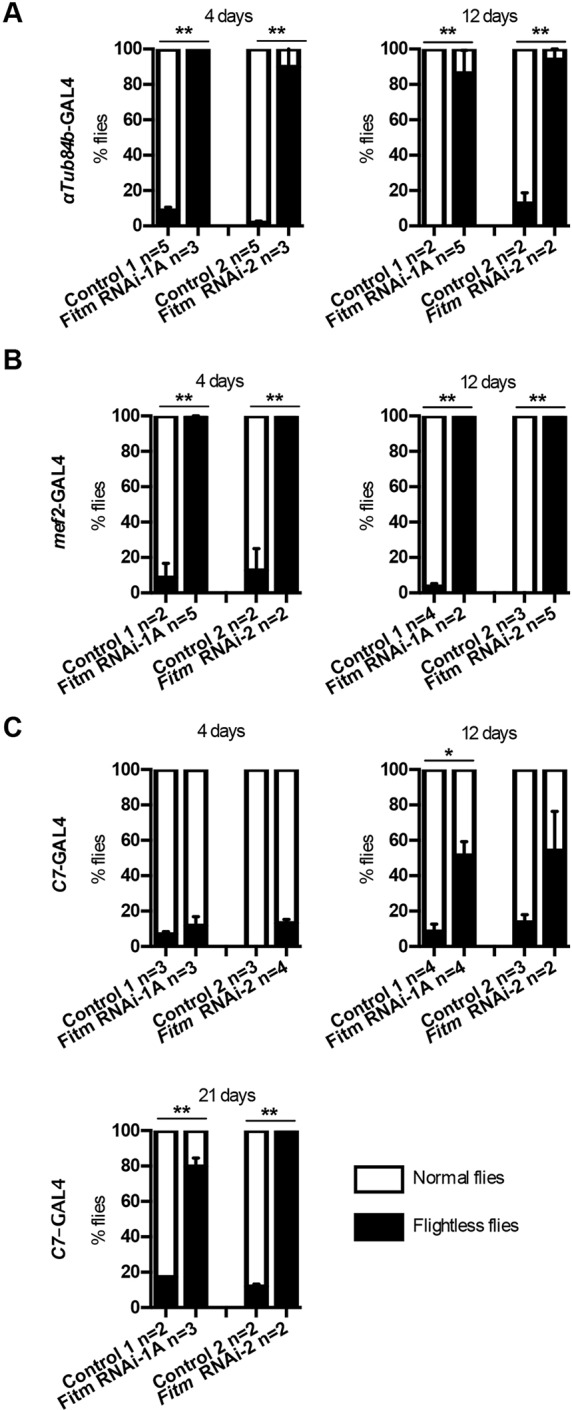
Knockdown of Fitm impairs locomotor abilities in Drosophila. Stacked bar graphs show the average percentage of flightless flies (black bars) and flies with normal flight responses (white bars). Error bars represent s.e.m. The indicated days represent days of age past eclosion. Fitm knocked down ubiquitously and preferentially in skeletal muscle with the αTub84B-GAL4 (A) and Mef2-GAL4 (B) promoters, respectively, and Fitm RNAi-1A and Fitm RNAi-2 showed significant locomotor impairment at all time points. (C) Fitm knockdown in the fat body (C7-GAL4 driver) using Fitm RNAi-1A and Fitm RNAi-2 revealed a progressive locomotor impairment evident at 12 days after eclosion as compared with corresponding age-matched control flies. The percentages of normal and flightless flies per experiment was used to determine statistical differences by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's correction for multiple testing, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. Average percentages are plotted in the graphs. The n refers to the number of experiments. Number and percentages of flightless and normal flies in each independent experiment can be found in Table S7.
