Fig. 4.
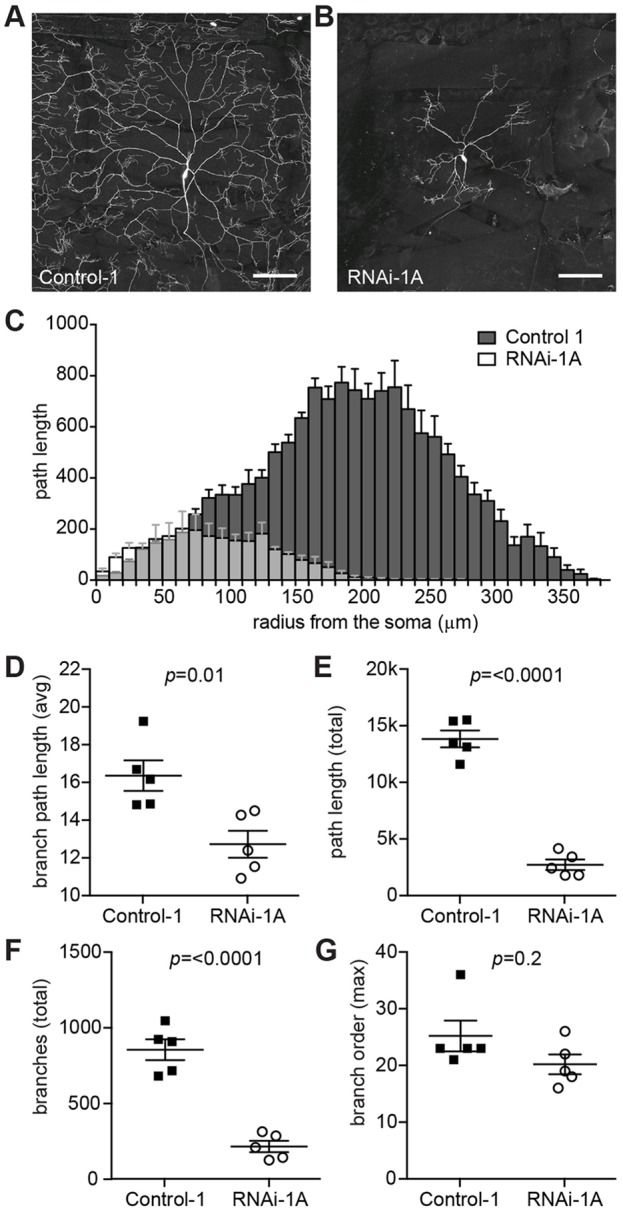
Fitm RNAi-1 knockdown in Drosophila interferes with morphology of nociceptive multi-dendritic sensory neurons. (A,B) Confocal projections of class IV da neurons within segment A3 of third instar larvae, visualized with the class IV da-specific drivers 477-GAL4 and ppk-GAL4 and UAS-mCD8::GFP. The ddaC neurons show abnormal dendritic morphology in a subset of Fitm RNAi larvae. (A) Control-1 shows ddaC contact to neighboring neurons. (B) Knockdown of Fitm in line RNAi-1A results in a severe outgrowth defect, observed in 5/18 larvae. The five highly abnormal neurons (see Fig. S6) were analyzed further, to test whether they significantly differ from the control. (C) Sholl analysis (Wearne et al., 2005) of control (n=5) and selected highly abnormal neurons (n=5) reveals defects as a measure of the soma distance. The Fitm RNAi-1A dendritic field coverage has a radius that is 60% the size of that of the control. (D-G) Quantitative analysis of dendritic trees reveals that the affected Fitm RNAi-1 neurons have (D) a reduced average branch path length (P=0.01), (E) a reduced accumulative branch path length (P≤0.0001), (F) a decreased number of branches (P≤0.0001), and (G) not significantly changed maximal branch order (P=0.2). Dorsal is up in A,B. Scale bar: 100 μm. Error bars in (D-G) indicate s.e.m. t-test between control and knockdown conditions was performed for each parameter to determine significance. P-values are depicted in each graph. Five neurons per strain, derived from five different larvae, were analyzed. The data were collected in two independent experiments. For underlying numerical data see Tables S8 and S9. More information about the depicted parameters can be found in Table S11.
