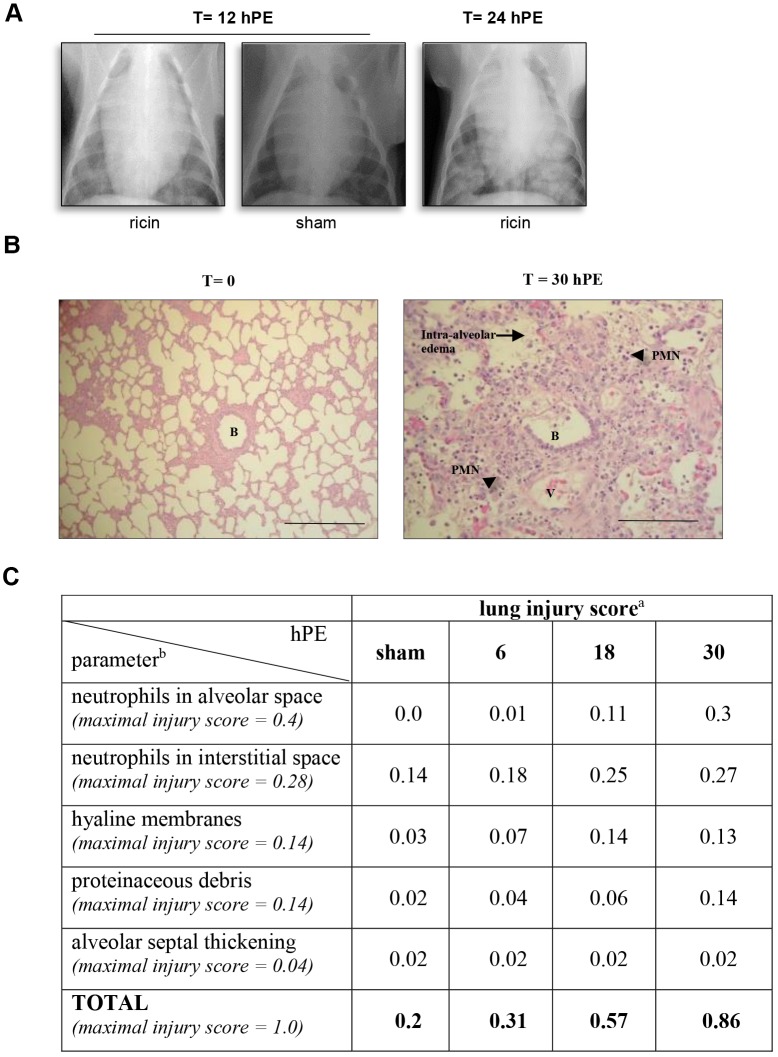
Fig. 4.
Lung injury following ricin intoxication. (A) X-ray. CXR radiographs were taken at 12 and 24 hpe to ricin (3 µg/kg body weight) and representative CXRs are shown. t=12 hpe ricin: representative CXR (1 of 3) of ricin-intoxicated pig at 12 hpe; t=24 hpe ricin: representative CXR (1 of 3) of ricin-intoxicated pig at 24 hpe; t=12 hpe, sham: CXR radiograph taken 12 h after sham intoxication. (B) H&E-stained lung section of a ricin-intoxicated pig. Lungs were removed at 30 hpe to ricin (3 µg/kg body weight) and subjected to histological analysis (400×). B, bronchiole; V, blood vessel; arrow, intra-alveolar edema; arrowheads, PMNs. Scale bars: 100 µm. (C) Lung injury scoring following ricin intoxication. aLung injury score was determined by scanning ≥20 random high-power fields (×400) of both lungs of two pigs per time point. bMaximal injury scores of the various parameters were assigned by the American Thoracic Society Committee (Matute-Bello et al., 2011) according to their relevance to experimental acute lung injury. n=8.