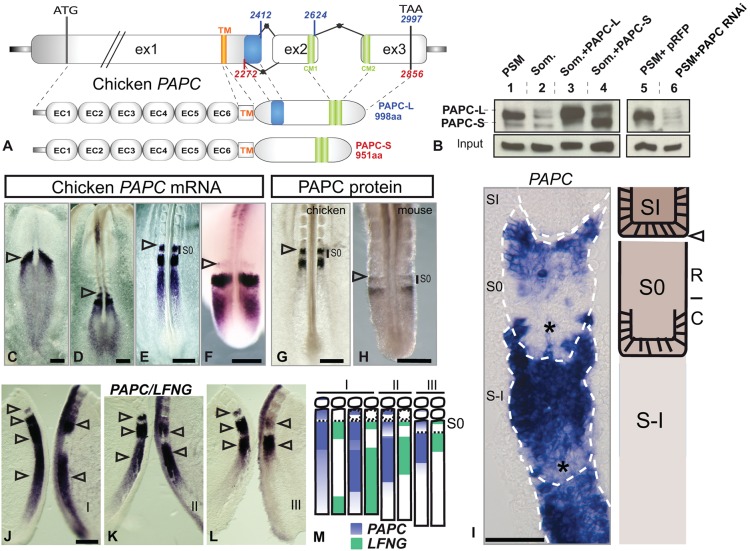
Fig. 1.
Characterization of chicken paraxial protocadherin. (A) Organization of the PAPC locus showing sequence features (in base pairs). The long (PAPC-L) and short (PAPC-S) isoforms differ by alternative splicing of the 3′ end of exon1 (blue box). CM1/2, conserved domains of δ-protocadherins (green boxes); EC, extracellular cadherin motif; ex, exon; TM, transmembrane domain. (B) Chicken PAPC protein expression by western blot on extracts of wild-type PSM (lane 1), wild-type somite (2), somites overexpressing PAPC-L (3) or PAPC-S isoform (4), and PSM expressing PAPC RNAi constructs (5,6). (C-H) PAPC mRNA expression in chicken embryo at stage 6HH (C), 6-somite stage (D), E2 (20-somite) embryo (E), E3 embryo (F), and of PAPC protein in E2 (20-somite) chicken embryo (G), and in mouse at E10.5 (H). Whole embryo is shown in C,D and detail of the posterior region showing the PSM in E-H. S0, forming somite. Arrowheads denote the last formed somite boundary. (I) Left: parasagittal section showing chicken PAPC mRNA expression in the anterior PSM (blue). Somite boundaries are delimited by white dashed lines. Caudal half somites lacking PAPC mRNA are indicated by asterisks. Right: corresponding diagram. C, caudal; R, rostral; S-I/0/I, somite -I/0/I. Arrowhead indicates the last formed somite boundary. (J-M) Direct comparison of PAPC and LFNG mRNA dynamics on bisected E2 (20-somite) chicken embryos (J-L; n=17) and corresponding scheme (M). Arrowheads denote expression stripes. Segmentation clock phases are indicated by roman numerals. (C-H,J-L) Dorsal views, anterior to the top. Scale bars: 200 µm (C-H,J-L); 50 µm (I).