FIG 1 .
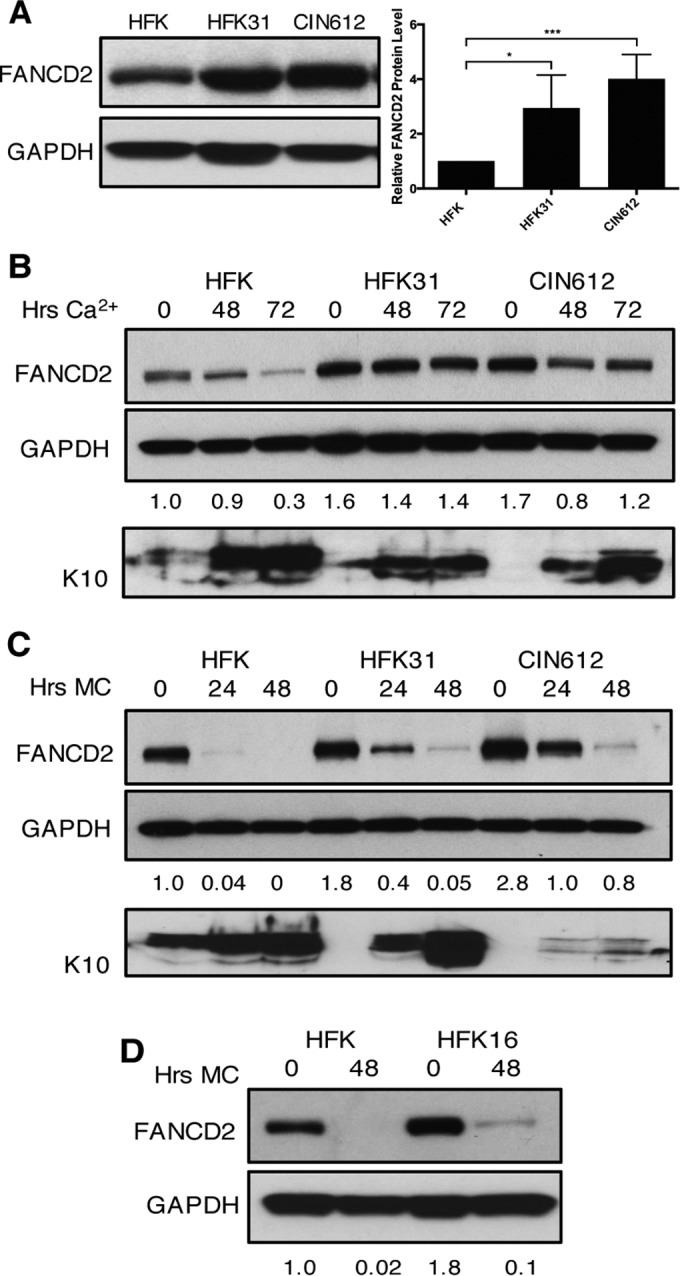
Levels of FANCD2 are increased in HPV-positive cells and remain elevated through differentiation. (A) Western blot analysis of FANCD2 levels in normal human foreskin keratinocytes (HFKs), HFKs stably transfected with HPV31 whole genomic DNA (HFK31), and CIN612 cells. The graph demonstrates FANCD2 protein levels relative to GAPDH and normalized to FANCD2 levels in HFKs across three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviations between experiments. A standard Student’s t test was used to determine statistical significance. *, P ≤ 0.05; ***, P ≤ 0.001. (B) Western blot analysis of FANCD2 levels in HFK, HFK31, and CIN612 cells that were differentiated in 1.5 mM calcium medium for 48 or 72 h. Epithelial differentiation was confirmed by levels of cytokeratin 10. (C) Western blot analysis of FANCD2 levels in HFK, HFK31, and CIN612 cells that were differentiated in 1.5% methylcellulose for 24 or 48 h. Epithelial differentiation was confirmed by levels of cytokeratin 10. (D) Western blot analysis of FANCD2 levels in HFK and HFKs stably transfected with HPV16 DNA that were differentiated for 48 h in 1.5% methylcellulose. Quantification of FANCD2 band intensity was determined by densitometry using Image Lab software relative to GAPDH and normalized to HFKs.
