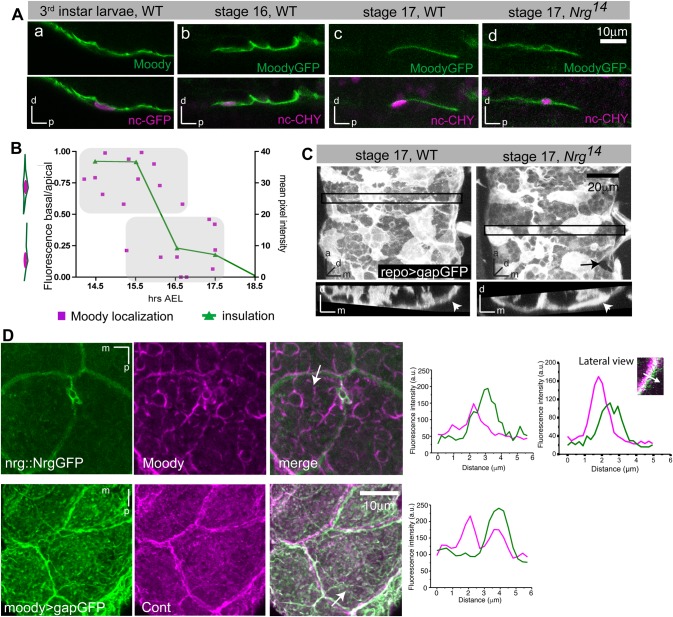
Fig. 5.
Fence function of SJs is required for establishment of polarized membrane compartments in SPG. (Aa) Immunohistochemistry against Moody and moody>ncGFP. Moody is enriched on the apical (i.e. nervous-system facing) side of SPG in third instar larva. (Ab-d) Live imaging of GFP-tagged Moody using MZ1251>moodyGFP, nuclearCherry. Moody is not polarized in stage 16 embryos, but localizes exclusively to the apical surface by stage 17. (Ad) In Nrg14 mutants, Moody fails to polarize. Lateral views of the CNS/hemolymph border with the CNS facing up in all images. (B) Quantification of MoodyGFP localization in WT. Polarization of MoodyGFP (magenta), computed as basal/apical ratio of fluorescence intensities, coincides with CNS insulation (green). Insulation was quantified by measuring the levels of fluorescent Dextran-TR diffusion into the CNS. (C) In Nrg14 mutants, the SPG epithelium forms largely normally (arrowheads), although small gaps in the epithelium remain visible (arrow). 17 h old embryos; glia are labeled by repo>gapGFP; top panels, ventral view; bottom panels, orthogonal view of areas indicated by black box; stack of 15 µm. (D) Both Moody and gapGFP are observed immediately adjacent to but not coincident with SJ components (Nrg::GFP or Contactin). Immunohistochemistry; ventral view of CNS; stacks of 10 µm; graphs show intensity profiles along the line marked by an arrow in the merged panels.