Fig. 7.
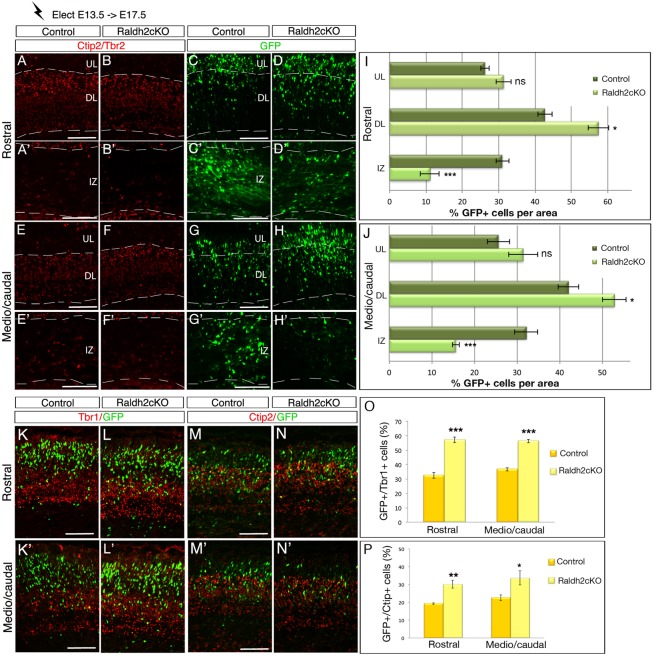
Lack of RA impairs cell migration of early-born cortical neurons. Brain sections from E17.5 mice electroporated at E13.5 with a GFP reporter construct were analysed for GFP (C-D′,G-H′), and by immunolabelling for Tbr2 and Ctip2 (A-B′,E-F′). Single-color immunolabelling for the two markers help to define the upper layers (UL) and deeper layers (DL) of the cortical plate and the intermediate zone (IZ). (I,J) Histograms depict the percentage of GFP-positive cells per zone (UL, DL and IZ) of the rostral (I) and caudal (J) levels of developing cortex. (K-L′,O) Quantification of GFP-positive cells (green) expressing Tbr1 (red) in the cortical plate of control and Raldh2cKO animals. (M-N′,P) Quantification of GFP-positive cells (green) expressing Ctip2 (red) in the cortical plate of control and Raldh2cKO animals. The histograms (O,P) show the percentage of double-labelled cells over GFP+ cells. Data presented as mean±s.e.m.; n=5 brains; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 by two-way ANOVA (I,J) and two-tailed Student's t-test (O,P). Scale bars: 100 μm.