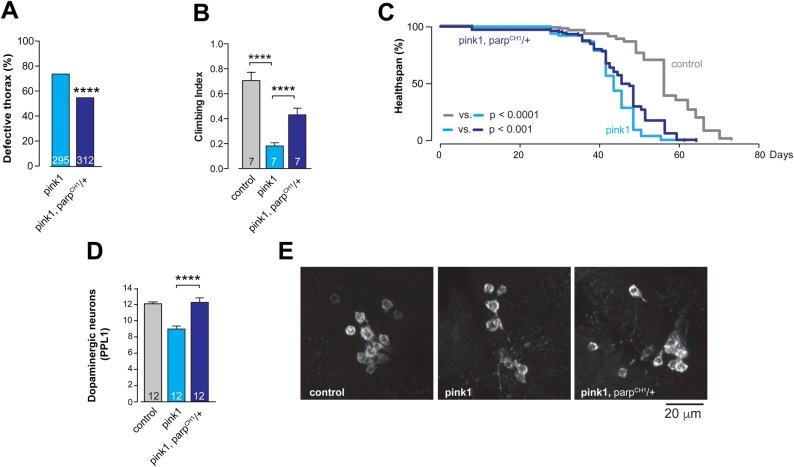
Fig. 4.
Parp mutation rescues pink1 mutant phenotype. (A) Parp mutation rescues the thoracic defect (asterisks, two-tailed chi-square test, 95% confidence intervals), (B) climbing ability (mean±s.d.; asterisks, two-tailed unpaired t-test) and (C) increases survival of pink1 mutants (n=130 for control, n=114 for pink1, and n=106 for pink1, ParpCH1/+; asterisks, log-rank Mantel-Cox test). (D) Parp mutation rescues the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the PPL1 cluster of pink1 mutant flies (mean±s.e.m.; asterisks, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison test). (E) Representative images of anti-tyrosine hydroxylase-stained PPL1 cluster neurons are shown for the indicated genotypes. Genotypes: control: w1118, pink1: pink1B9, pink1, parpCH1/+: pink1B9, ParpCH1/+. Dataset in D labelled ‘control’ has been previously published in Lehmann et al. (2016), as data were obtained as a single experimental set before statistical analysis.