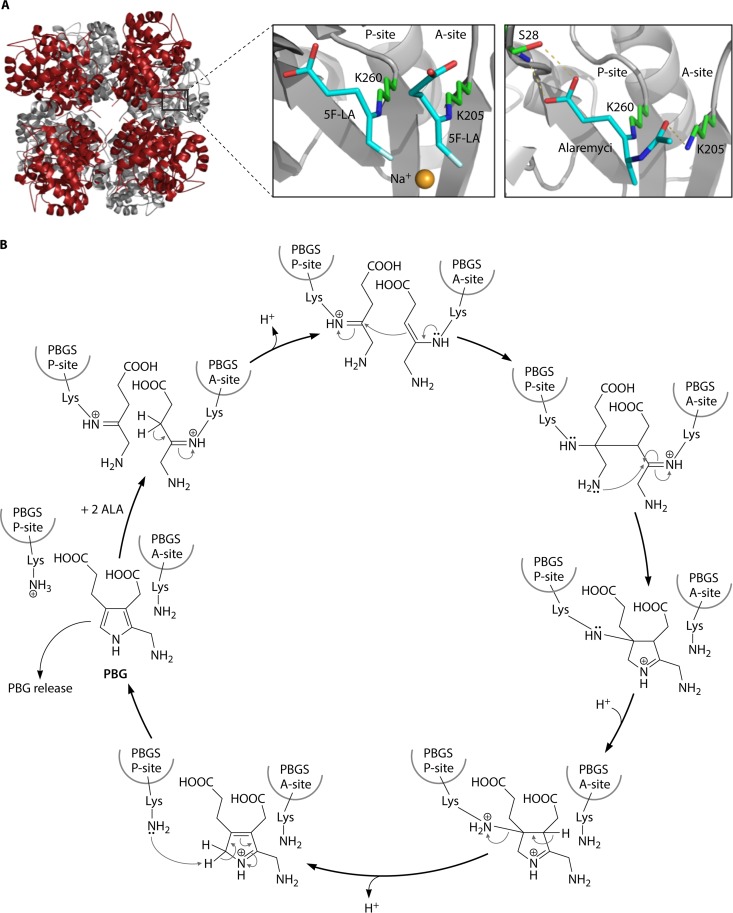
FIG 6.
Porphobilinogen synthase (PbgS). (A, left) Crystal structure of P. aeruginosa PbgS showing the octameric assembly of the protein representing a tetramer of homodimers. (Top right) In the active site of P. aeruginosa PbgS, two molecules of the substrate analog 5-fluorolevulinic acid (5F-LA) were observed to bind covalently to the enzyme through Schiff bases, with the catalytically essential lysine residues supporting a double-Schiff-base mechanism. (Bottom right) The antibiotic alaremycin was also observed to bind covalently to the enzyme through a Schiff base with the P-site lysine. (Adapted from reference 14.) (B) Proposed reaction mechanism by which PbgS catalyzes the asymmetric condensation of two ALA molecules to the pyrrole porphobilinogen (see the text for a detailed explanation). (Adapted from reference 97.)