Figure 5.
Long-Term Proliferating GMP-like Cells Derived from C/EBPβ-Transduced B Cells
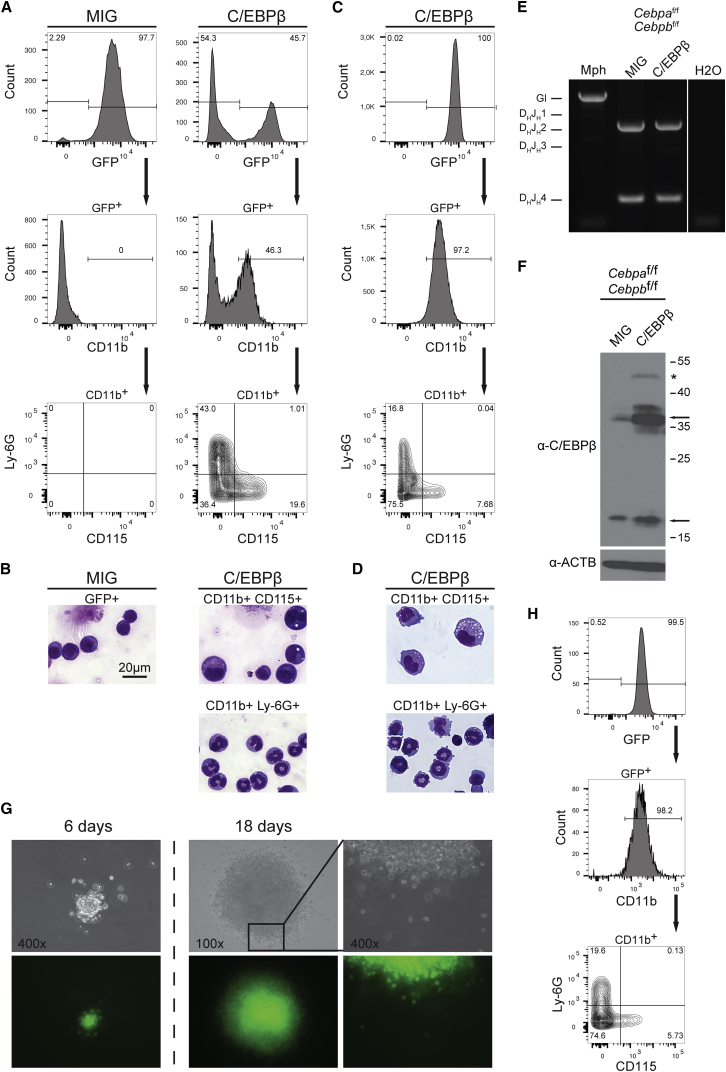
(A) Cebpaf/f;Cebpbf/f B cells transduced with C/EBPβ or vector control (MIG), sorted after 24 hr, and recultured. Flow cytometric analysis of myeloid surface markers was performed after 6 days. Gating strategy is indicated by arrows.
(B) May-Grünwald staining of macrophage (CD11b+CD115+) or granulocyte (CD11b+Ly-6G+) marker-sorted C/EBPβ-transduced cells from (A) and GFP+-purified empty vector (MIG)-transduced cells as control.
(C and D) Flow cytometry analysis (C) and May-Grünwald staining (D) according to (A) and (B) of non-purified C/EBPβ-transduced cells 6 weeks after removal of β-mercaptoethanol.
(E) Analysis of immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) rearrangement of long-term C/EBPβ-transduced cells or MIG-transduced controls. Monocytic Raw264.7 (Mph) cells served as a control for IgH germ line (Gl) configuration.
(F) Immunoblot analysis of C/EBPβ from protein lysates of long-term C/EBPβ- or empty vector (MIG)-transduced B cells. Arrows indicate C/EBP isoforms; asterisk indicates the size of transgene.
(G) Colony formation from single cells. Phase contrast (top) and fluorescent signal (bottom) micrographs of a C/EBPβ-transdifferentiated B cell colony. Clonogenic growth is shown at days 6 and 18. Magnification of inset area focuses on the border of the colony.
(H) Flow cytometric characterization of the recultured cell clone derived from (G) using myeloid markers.
See also Figure S5.