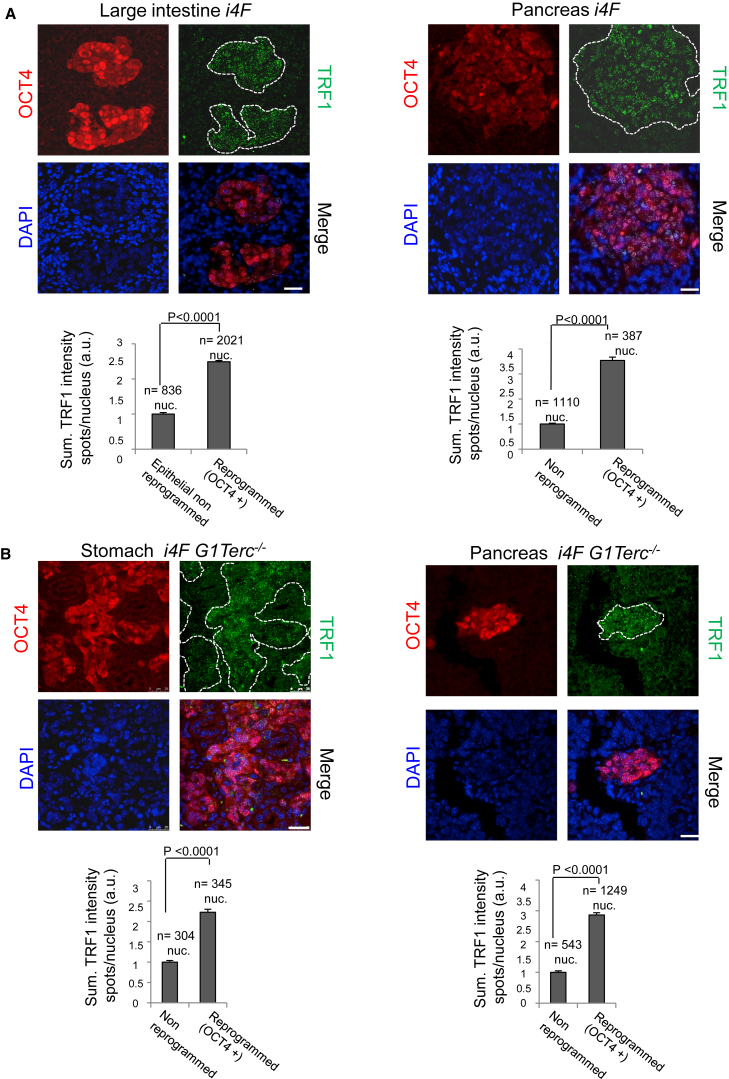
Figure 4.
Increased TRF1 Expression during In Vivo Reprogramming Correlates with OCT4 Expression and Is Uncoupled from Telomere Length
(A) Upper: representative images of double immunofluorescence against OCT4 (red) and TRF1 (green) proteins in (left) the large intestine and (right) the pancreas of reprogrammable mice after induction of in vivo reprogramming. A strong correlation between the presence of OCT4 and high TRF1 expression can be observed. Lower: quantification of TRF1 expression in in vivo reprogrammed cells and the corresponding non-reprogrammed control cells. Scale bars, 25 μm. Error bars denote SE. Statistical analysis by Student's t test. n, number of nuclei. Number of mice analyzed = 3.
(B) Upper: representative images of double immunofluorescence against OCT4 (red) and TRF1 (green) proteins in (left) the stomach and (right) the pancreas of i4F G1Terc−/− reprogrammable mice after induction of in vivo reprogramming. High TRF1 levels are observed in the in vivo reprogrammed areas even in the absence of a functional telomerase enzyme. Lower: quantification of TRF1 expression in in vivo reprogrammed cells and the corresponding non-reprogrammed control cells.
White dashed lines mark the reprogrammed area. Scale bars, 25 μm. Error bars denote SE. Statistical analysis by Student's t test. n, number of nuclei. Number of mice analyzed = 3.
See also Figures S1 and S3.