Figure 4. Mir-203 could directly be upregulated by KLF4 and inhibit survivin expression.
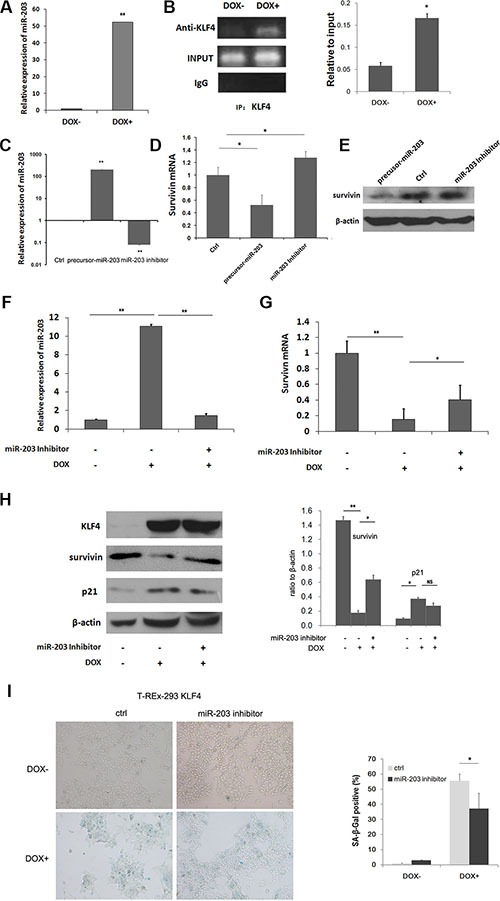
(A) Real-time PCR analysis of relative miR-203 expression upon DOX treatment of T-REx-293 KLF4 cells. Bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). **p < 0.01. (B) PCR analysis of direct binding of KLF4 to KLF4 binding sites of miR-203 promoter in T-REx-293 KLF4 cells with/without DOX treatment. Anti-KLF4 antibody or mouse IgG were used for immunoprecipitation. Input DNA was used as positive control, and immunoprecipitation of IgG as negative control. (C) Detection of miR-203 in T-REx-293 cells transfected with pre-miR-203 precursor or miR-203 inhibitor by qRT-PCR. Bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). **p < 0.01. (D) Real-time PCR analysis of survivin mRNA regulated by miR-203. Bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05,**p < 0.01. (E) Western blotting analysis of protein expression of survivin. (F) Expression of miR-203.T-REx-293 KLF4 cells were pre-transfected with miR-203 inhibitor or its scrambled control for 24 h, and then treated with DOX for 24 h. Bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). **p < 0.01. (G) mRNA level of survivin detected by qRT-PCR. Bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05,**p < 0.01. (H) Survivin and p21 protein expression analyzed through Western blotting. (I) Representative SA-β-gal staining photos(magnification 100×) and percentage of senescence cells. T-REx-293 KLF4 cells were pre-transfected with miR-203 inhibitor or its scrambled control for 24 h, and then induced by DOX for 72 h. Bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 3).
