Figure 4.
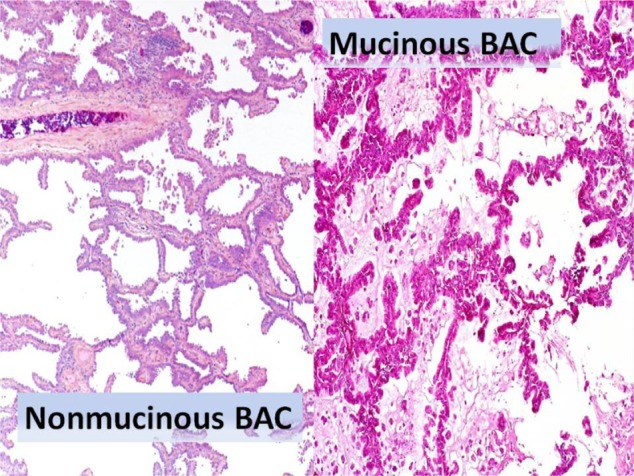
Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC, mucinous and non-mucinous variants) histologic specimens. BAC arises from alveolar walls as a noninvasive tumor with lepidic spread (along alveolar septa); no stromal, vascular, or pleural invasion is seen. Microscopically BAC is composed of tall, columnar cells lining alveolar septa and projecting into spaces with papillary projections, but underlying lung architecture is preserved; variable anaplasia but usually well differentiated. Non-mucinous type is composed of cuboidal cells with bright eosinophilic cytoplasm, prominent nucleoli, and nuclear atypia; apical spouts and hobnail cells are often present. Mucinous type is composed of well-differentiated columnar cells containing mucin that line respiratory spaces; tumor cells are associated with bronchioles, not bronchi; demarcation between normal and tumor cells is usually sharp.
