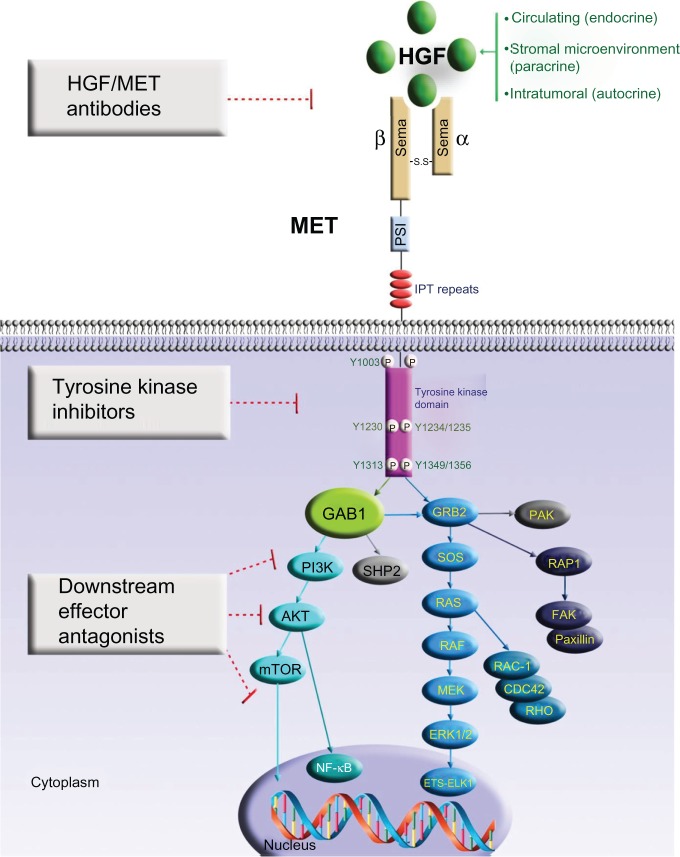
Figure 1.
MET receptor signaling and strategies of therapeutic inhibition in lung cancer.
Notes: Aberrant hepatocyte growth factor stimulation of MET in human cancer can occur by aberrant autocrine (intratumoral), paracrine (stromal microenvironmental), or endocrine (circulatory) loop signal activation. Upon hepatocyte growth factor binding to the Sema domain, the MET receptor dimerizes, which leads to autophosphorylation of intracellular kinase domain tyrosine residues Y1230/Y1234/Y1235, followed by the phosphorylation of Y1349 and Y1356. MET activation results in the recruitment and activation of downstream adaptor proteins and kinase targets. This results in a multitude of effects such as increased cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, scattering, motility, survival, extracellular matrix remodeling, and changes in metabolism. MET signaling is important in mediating tumor addiction/dependence and tumor expedience. Therapeutic intervention strategies to inhibit MET receptor oncogenic signaling cascade include blocking ligand-receptor interaction, preventing receptor dimerization, blocking MET kinase intrinsic activity, and inhibiting specific downstream signal transducers.
Abbreviations: AKT, protein kinase B; CDC42, cell division control protein 42 homolog; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; ETS-Elk1, E 26-like transcription factor 1; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GAB1, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2-associated adaptor protein 1; GRB2, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IPT, immunoglobulin-like–plexin transcription factor; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; P, phosphorylation; PAK, p21-activated kinase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PSI, plexin–semaphorin–integrin; RAC-1, Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1; RAF, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; RAP1, Ras-related protein 1; RAS, rat sarcoma oncogene homolog; RHO, Ras homolog; SHP2, Src homology region 2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 2; SOS, Sos protein.