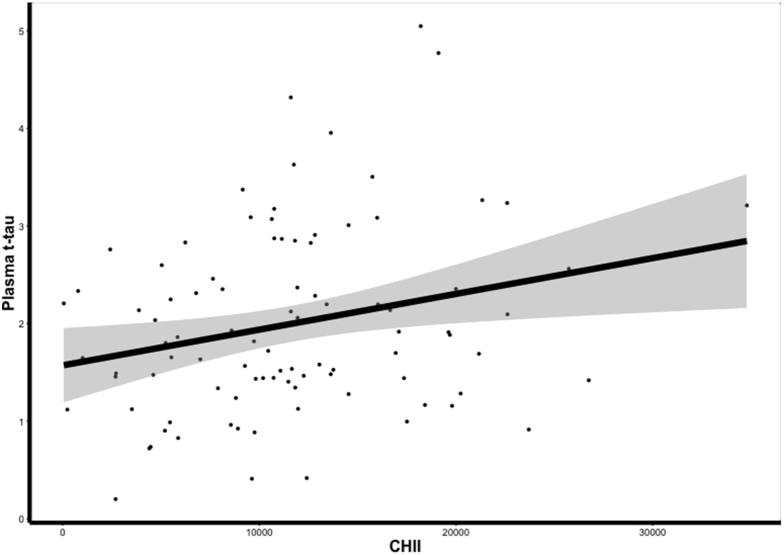
Fig. 2.
Greater exposure to repetitive head impacts is associated with higher later-life concentrations in plasma total tau (t-tau). The scatter plot depicts the relationship of the residuals between the cumulative head impact index (CHII) and plasma t-tau after controlling for age and body mass index, which was significant (P = .0137). Because the residuals resulted in negative values on the x-axis, a constant value was added to y- and x-axis values to facilitate interpretation. X-axis values are scores on the CHII, with higher scores representing greater exposure to repetitive head impact. Y-axis values are plasma t-tau concentrations in pg/mL units. Shaded region represents standard error.