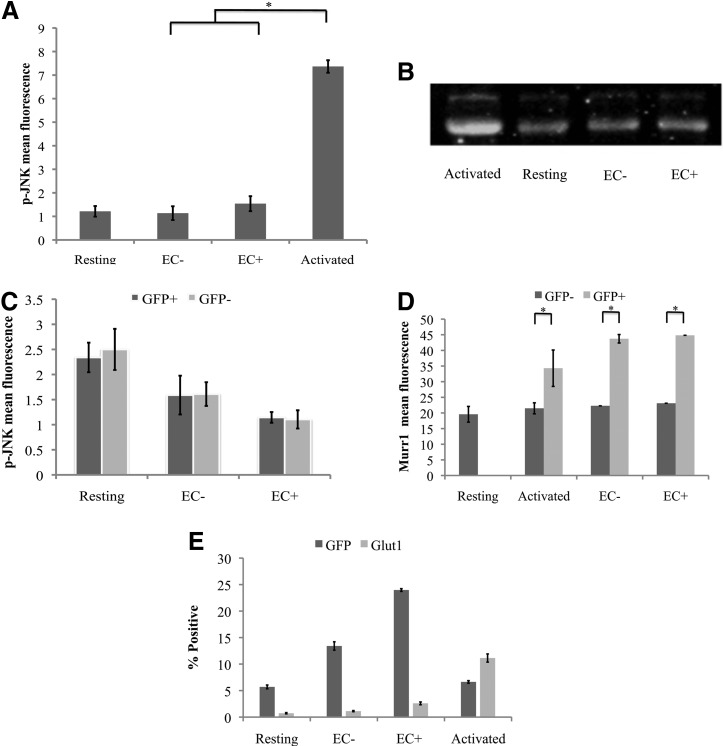
FIG. 7.
JNK, Murr1, and Glut1 expression in resting T cells does not change after stimulation by EC. (A) Resting T cells were cultured alone, with EC+/−, or with PMA and Ionomycin. p-JNK intracellular staining was done 4 days later for PMA/I-activated cells, and 7 days later for resting T cells cultured alone or with EC− and EC+. Samples were taken in duplicates, and means ± standard deviations are plotted. Data shown are the representative of two independent experiments yielding similar results. (B) In a similar way, resting CD4+ T cells were cultured alone, activated with PMA/I, or cocultured with EC− or EC+ and analyzed for JNK expression through western blot analysis. (C) Resting CD4+ T cells were cultured alone or with EC− or EC+ and infected with a GFP reporter virus the next day. Intracellular staining was done on day 7 postinfection to measure p-JNK expression. GFP+ cells were productively infected, and GFP− cells were not productively infected. Samples were taken in duplicates, and means ± standard deviations are plotted. (D) Resting T cells cultured alone or with EC+/− or activated with PMA/I. Murr1 expression was determined by intracellular staining 7 days after infection. Samples were taken in duplicates, and means ± standard deviations are plotted. Data shown are the representative of two independent experiments yielding similar results. (E) Resting CD4+ T cells were cultured alone, activated by PHA, or stimulated by EC+/−. Cells were infected with a GFP reporter virus. GFP expression and GLUT1 staining were performed 3 days after infection for PHA-activated cells and 7 days after infection for resting cells that were unstimulated or stimulated by EC. Samples were taken in triplicates, and means ± standard errors are plotted. Data shown are the representative of three independent experiments yielding similar results. *Student t-test; p < .05. Glut1, glucose transporter 1; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; PHA, phytohemagglutinin; p-JNK, phosphorylated JNK.