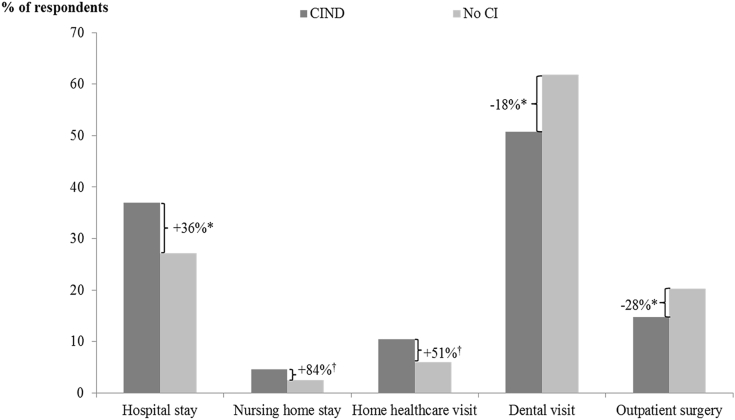
Fig. 2.
Difference in health care resource use among matched CIND and no CI cohorts—during the index wave. *P < .05; †P < .1. Relative difference in rates was calculated by dividing the difference between proportions of CIND respondents with a given health care resource use and corresponding proportions among matched no CI respondents by corresponding proportions among matched no CI respondents. Respondents with CIND were matched 1:1 to those with no CI using propensity score–based optimal matching techniques. Propensity scores were calculated using logistic regression models that estimated the probability of having CIND as a function of age, gender, race, region, years of education, marital status, year of index wave, and presence of stroke/TIA. P-values were calculated using logistic regression models to account for complex survey design elements and correlation between matched pairs. Abbreviations: CI, cognitive impairment; CIND, cognitive impairment with no dementia.