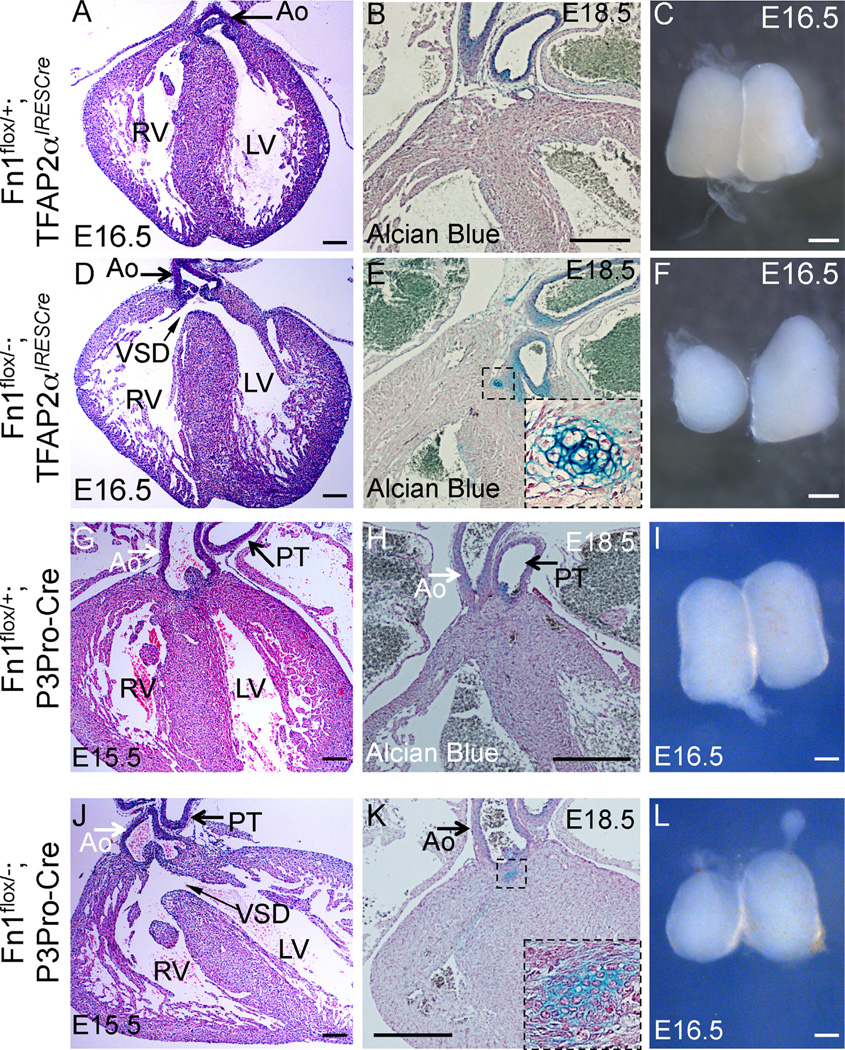
Fig. 4.
Cardiovascular and thymus defects in Fn1flox/−; TFAP2αIRESCre mutants at late gestation. (A–C) Fn1flox/+; TFAP2αIRESCre controls; (D–F) Fn1flox/−; TFAP2αIRESCre mutants; (G–I) Fn1flox/+; P3Pro-Cre+ controls; and (J–L) Fn1flox/−;P3Pro-Cre+ mutants. All sections were cut in coronal orientation. (A, D, G, J) - H&E staining. Slim arrows in (D) and (J) point to the membranous ventricular septal defect (VSD). Ao - ascending aorta. PT - pulmonary trunk, RV-right ventricle, LV - left ventricle. (B, E, H, K) - Alcian blue and nuclear fast red staining. Cartilage in the mutants is stained in blue (dashed box, expanded in insets of E and K). (C, F, I, L) - whole isolated thymus lobes. Mutants display hypoplastic and asymmetric thymus lobes (F, L). Scale bars: 100 µm in (A), (D), (G), and (J); 200 µm in (B), (E), (H), and (K); 500 µm in (C), (F), (I), and (L).