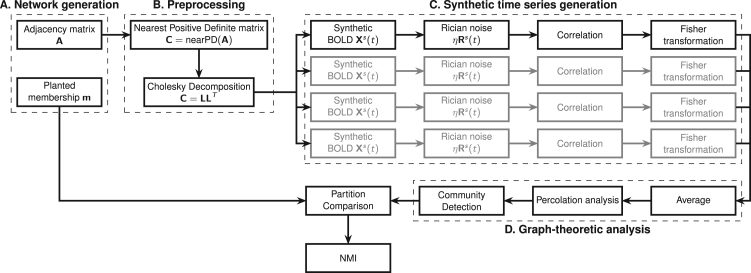
Fig. 1.
Flowchart of the generation and analysis of the synthetic datasets. In A the network with a pre-defined community structure is generated. The adjacency matrix is then processed in block B to obtain the nearest positive definite matrix for the Cholesky decomposition. This enables the generation of node-wise time-courses into which different levels of noise can be injected. The procedure is repeated multiple times to generate different instances (mimicking different subjects in the sample). Finally, correlation matrices are calculated for each instance (block C), and Fisher transformed to calculate the average adjacency matrix for analysis by community detection algorithms (block D). Lastly, resulting partitions are compared with the original, planted one in terms of NMI.