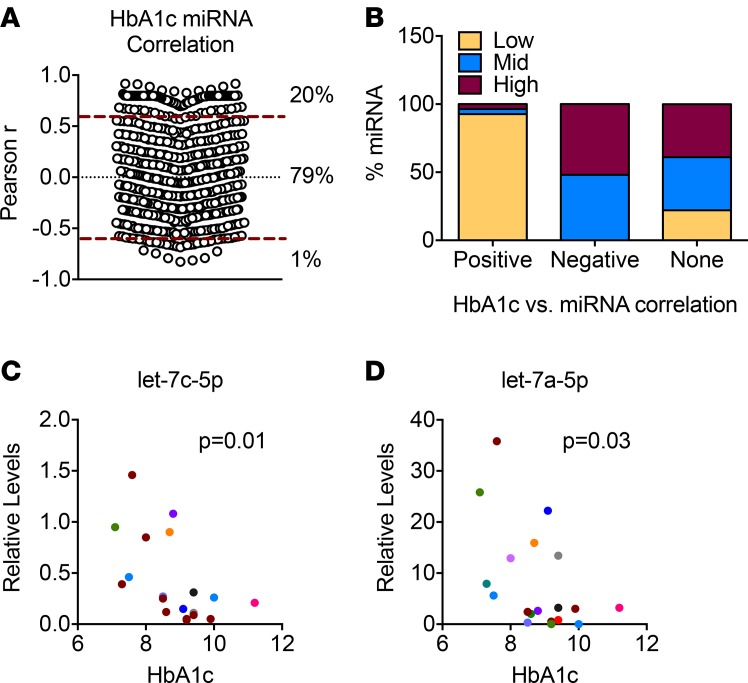
Figure 7. Correlation between miRNAs and hemoglobin A1c levels.
(A) A Pearson’s correlation was performed to determine the relationship between 634 miRNA levels and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels in 10 serum samples from children with type 1 diabetes (T1D). Twenty percent of all miRNAs correlated positively with HbA1c levels, whereas 1% displayed negative correlation. P ≤ 0.05 was considered significant. (B) miRNAs were classified into 3 groups based on their circulating levels: low, mid, and high. The percentage of miRNAs from each class contributing to positive, negative, or no miRNA-HbA1c association is shown. (C and D) Let-7c-5p and let-7a-5p levels were quantified using quantitative PCR (qPCR) with locked nucleic acid–enhanced primers in serum samples from a second cohort of patients with T1D, and correlation with HbA1c levels is shown. Cycle 30 (Ct = 30) was arbitrarily set as 1. Data was analyzed using Pearson`s correlation and 2-tailed P values are indicated.