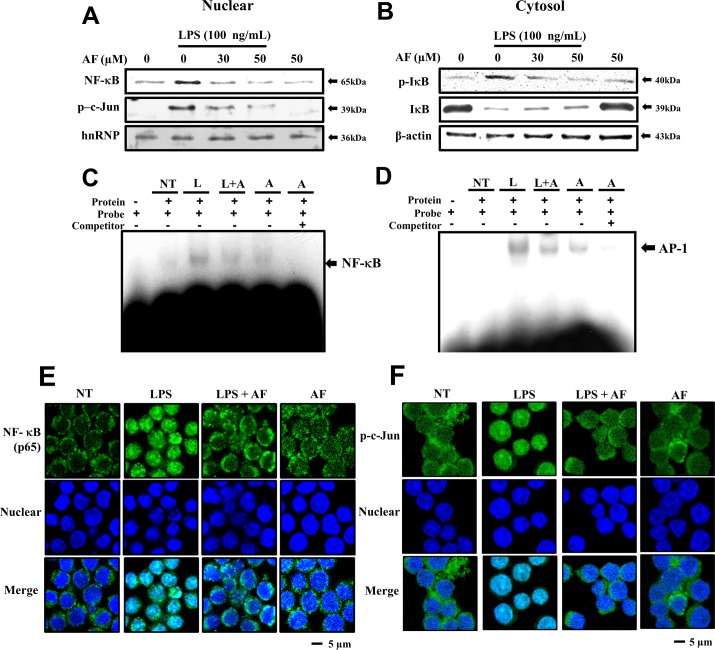
Fig 5. Effects of AF on LPS-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB and AP-1 in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.
Cells were treated in the presence or absence of various concentrations (0–50 μg/ml) of AF for 30 min and further incubated with or without 100 ng/ml of LPS for 15 min. Then, the cells were harvested and separated into nuclear (A) and cytosolic extracts (B), as described in the Methods section. The protein extracts were separated on SDS-PAGE gels and immunoblotted using Western blot analysis. The antibodies used were anti-NF-κB, -p-c-Jun, -hnRNP, -IκB, and -β-actin. hnRNP and β-actin were used as controls for nuclear- and cytosol-specific proteins, respectively. (C), (D) EMSA showing the reduction in NF-κB and AP-1 DNA binding activity in nuclear proteins. Cells were prepared by stimulation with 100 ng/mL LPS for 15 min and pre-treated with 50 μM AF for 30 min. (E), (F) The translocation of NF-κB (p65) and AP-1 to the nucleus was analyzed by confocal microscopy. Macrophages were immunostained using FITC for NF-κB and AP-1 and Hoechst to label nuclei. White scale bars, 5 μm. NT, no treatment; A, AF; L, LPS; L+A, LPS with AF.