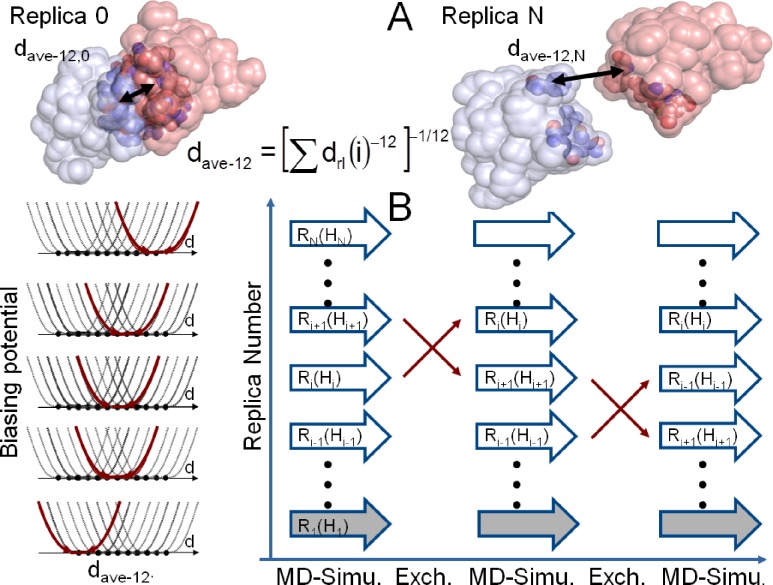
Fig 1. Illustration of the RP-REMD-Dock approach.
(A) Based on the accessible surface of the two isolated partner molecules two surface groups of atoms are defined. The 1/d-12 weighted distance is mainly determined by the closest contacts between the two groups and is used to define biasing penalty potentials for each replica (illustrated in B). The harmonic potentials allow for each replica a range of closest distances between the two partners such that the lower replicas allow close contacts without penalty but the higher replicas penalize such contacts by a quadratic function and push the partners on average slightly away from each other. The actual quadratic biasing potential in each replica run is illustrated in red (bold line), the range of potentials is indicated a thin lines. Since the allowed distance intervals overlap significantly between neighboring replicas a high acceptance rate for Hamiltonian replica exchanges leads to quick exploration of the biomolecular surfaces (replica scheme in the right panel).