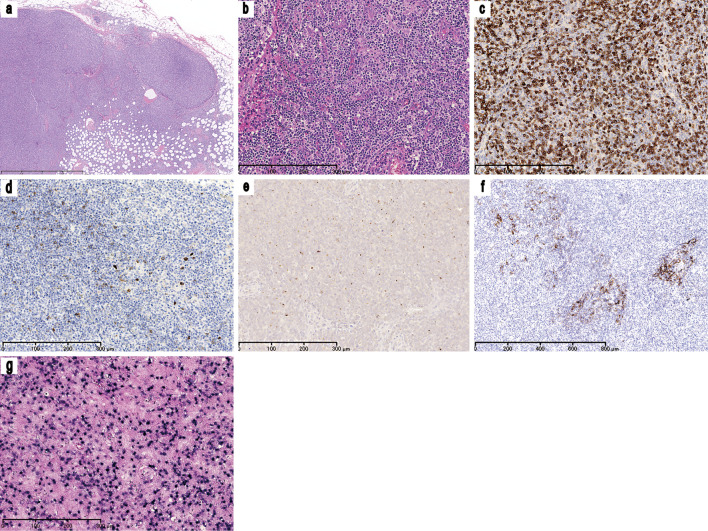
Figure 1.
Inguinal lymphoid biopsy. (a) A low power view of an inguinal lymph node biopsy specimen [Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining, ×25]. The normal lymph node architecture is almost completely effaced and the diffuse infiltration of lymphoid cells is observed. (b) A moderate-power view of the inguinal lymph node biopsy specimen (H&E staining, ×100). The aggregation of medium-sized atypical lymphoid cells and marked vascular proliferation can be observed. The neoplastic lymphoid cells have a clear to pale cytoplasm and convoluted nuclei with dispersed chromatin. Immunohistochemical staining for (c) CD3 (×100), (d) CD10 (×100), (e) CXCL13 (×100), and (f) CD21 (×50) revealed that most of the neoplastic cells showed CD3 positivity; the cells were negative for CD10 expression but some expressed CXCL13. The CD21 immunohistochemistry highlights the expansion of follicular dendritic cells. (g) EBV EBERin situ hybridization (×100) showing the marked infiltration of EBV-positive B cells. CD: Cluster of differentiation, CXCL: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand, EBER: Epstein-Barr-virus-encoded small RNA, EBV: Epstein-Barr virus