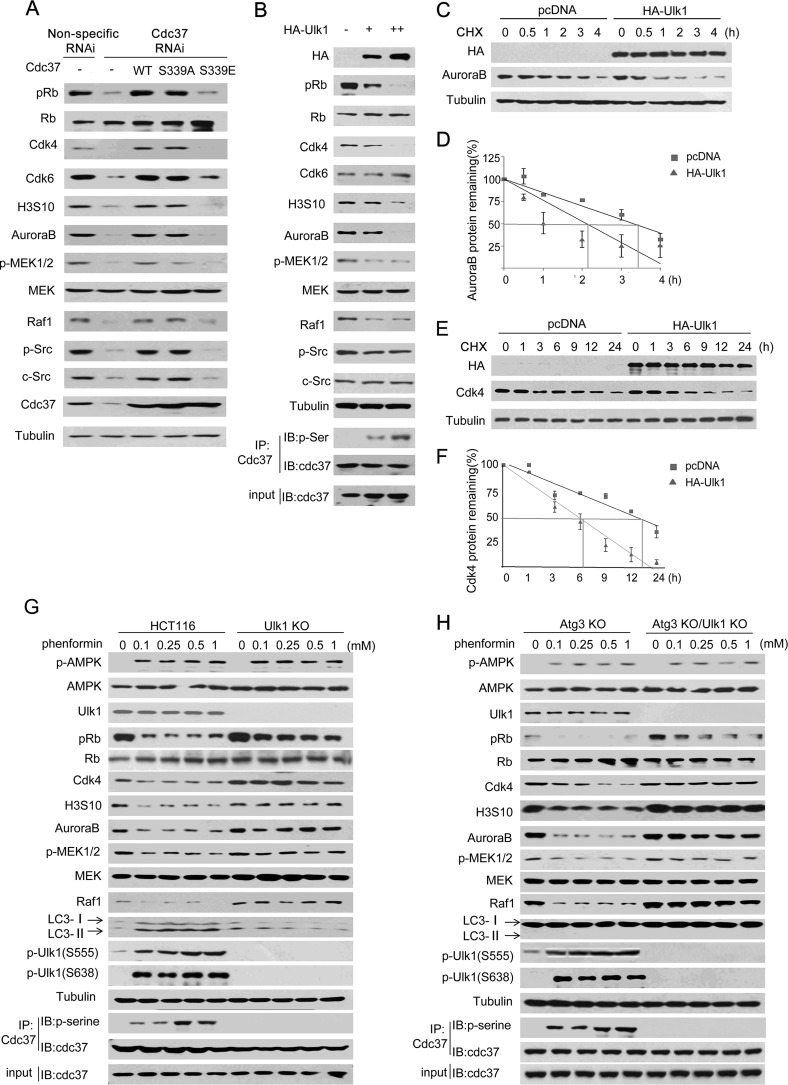
FIGURE 3.
Ulk1 suppressed the stability of Cdc37's clients. A, a set of RNAi-resistant rescue forms of Cdc37 plasmids were transfected into stable Cdc37-RNAi HCT116 cells. Western blotting was then performed to detect Cdc37 clients and their targets. B, different amounts HA-Ulk1 plasmid were transfected into Ulk1-KO HCT116 cells. Western blotting (IB) was then performed to detect Cdc37's clients and their targets. IP, immunoprecipitation. C–F, HA-Ulk1 plasmid or an empty plasmid was transfected into Ulk1 KO HCT116 cell. 24 h after transfection cycloheximide (CHX) was added at 10 μg/ml for different times as indicated. Western blotting was then performed to detect AuroraB (C) or CDK4 (E). The line graph shows the change in AuroraB (D) or CDK4 (F) levels at different times. G, wild-type and Ulk1-KO HCT116 cells were treated at different concentrations of phenformin for 24 h. H, Atg3-KO and Atg3-KO/Ulk1-KO HCT116 cells were treated at different concentrations of phenformin for 24 h.