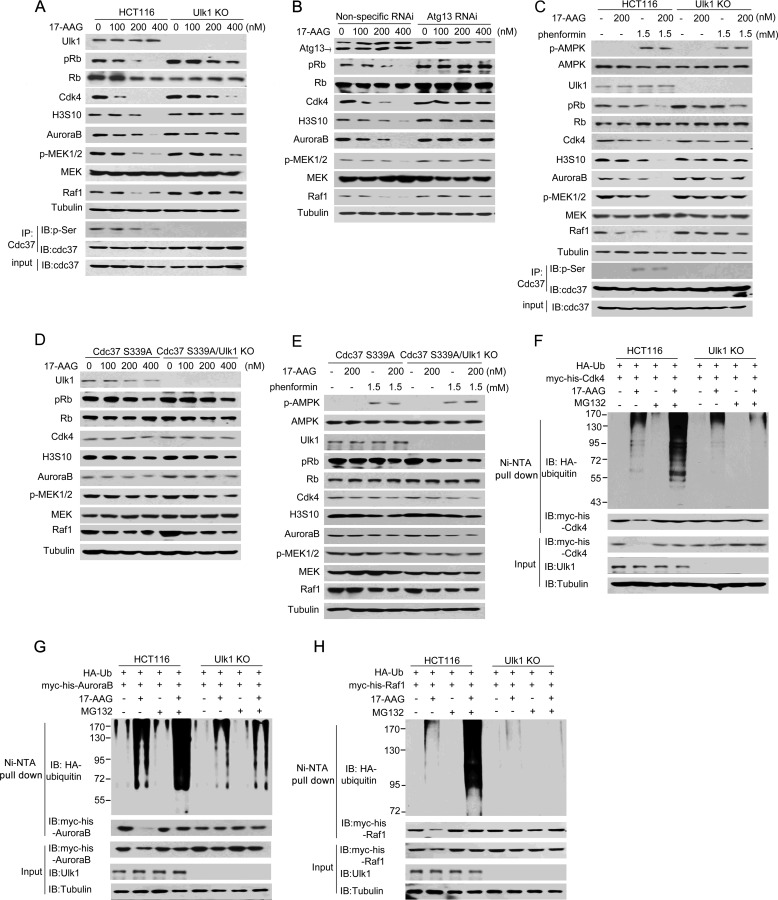
FIGURE 5.
Ulk1 is involved in the 17-AAG-induced degradation of several kinase clients of Cdc37. A, wild-type Ulk1 or an empty plasmid was stably transfected into Ulk1-knock-out HCT116 (Ulk1 KO) cells. Cells were treated at different concentrations of 17-AAG for 12 h, and proteins were then extracted for Western blot (IB). IP, immunoprecipitation. B, Atg13 RNAi was performed in Ulk1(WT)-expressing HCT116 cells. Cells were treated at different concentrations of 17-AAG for 12 h, and proteins were then extracted for Western blotting. C, wild-type and Ulk1-KO HCT116 cells were treated with the combination of 17-AAG and phenformin for 12 h. Proteins were then extracted for Western blotting. D, RNAi-resistant rescue form of Cdc37(S339) plasmid was transfected into Cdc37-KD or Cdc37-KD/Ulk1-KO HCT116 cells. Cells were treated at different concentrations of 17-AAG for 12 h, and proteins were then extracted for Western blotting. E, RNAi-resistant rescue form of Cdc37(S339) plasmid was transfected into Cdc37-KD or Cdc37-KD/Ulk1-KO HCT116 cells. Cells were treated with the combination of 17-AAG and phenformin for 12 h. Proteins were then extracted for Western blotting. F–H, Ulk1-expressing and Ulk1-KO HCT116 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. 24 h after transfection cells were treated for 12 h with MG132 and/or 17-AAG. Then CDK4 (F), AuroraB (G), and Raf-1 (H) conjugated to ubiquitin was purified by using Ni-NTA beads under denaturing conditions and then detected by Western blotting.