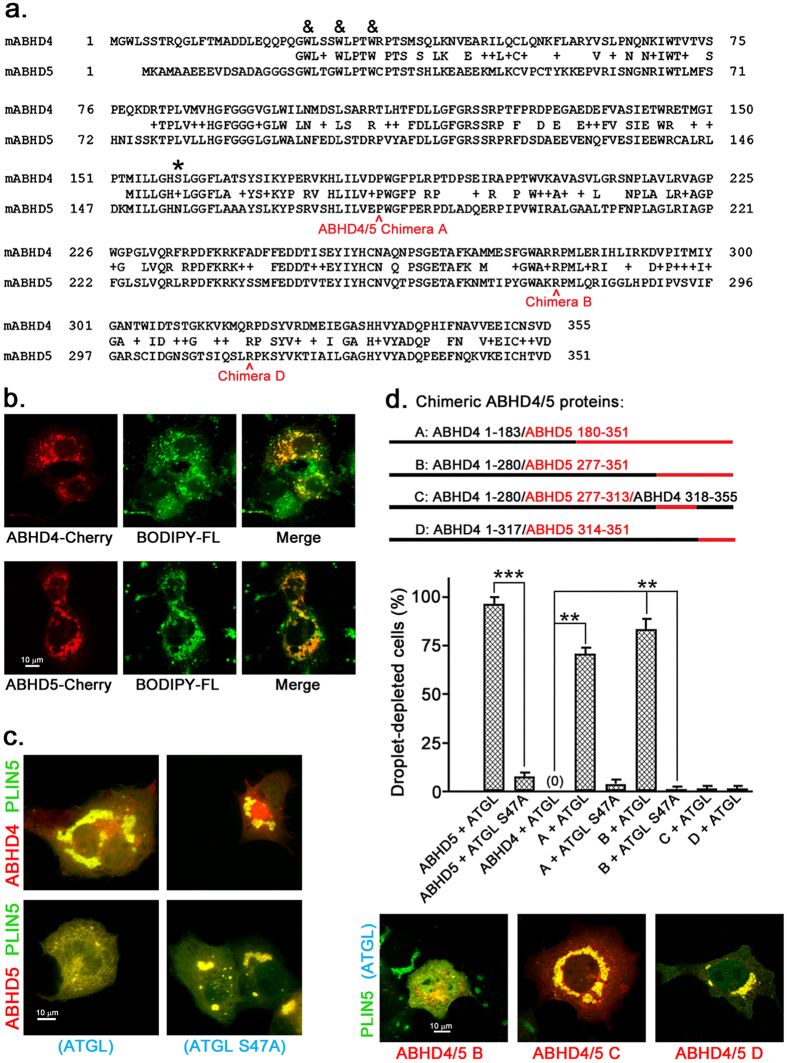
Figure 1. Chimeric ABHD4 1–280/ABHD5 277–351 activates ATGL-dependent lipolysis.
(a) Sequence comparison of mouse ABHD4 and ABHD5. & indicates common tryptophans required for LD localization of ABHD5, while the active site serine present in ABHD4 but not ABHD5 is indicated by *. In this figure and subsequent figures, ABHD proteins are from mouse and numbering of amino acids refers to the mouse protein unless indicated otherwise. PLIN5 and ATGL are also from mouse unless indicated otherwise. (b) ABHD4 associates with LDs. Cos7 cells transfected with ABHD4-mCherry or ABHD5-mCherry were lipid loaded overnight then stained with LD marker BODIPY-Fluorescein. This experiment was performed twice with the same results. (c) ABHD4 does not activate lipolysis. Cos7 cells transfected with ABHD protein-mCherry, PLIN5-EYFP, and ATGL-CFP or ATGL S47A-CFP (lipase inactive) were lipid loaded overnight then fixed. This experiment was repeated more than three times with the same results. In this experiment and subsequent experiments, Cos7 cells were co-transfected with PLIN5-EYFP to mark LDs and facilitate their formation, as described previously16. (d) Analysis of chimeric ABHD4/ABHD5 protein lipolysis activation. In this experiment and all subsequent experiments utilizing this assay (Figs 2, 3 and 7 and S1), only cells visibly expressing all three proteins (ABHD protein-mCherry, PLIN5-EYFP, and ATGL-CFP or ATGL S47A-CFP (lipase inactive)) were scored by an observer blinded to the transfection conditions. In (b–d), scale bars = 10 μm. Values are means ± SEM from three independent experiments. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.