Fig. 1.
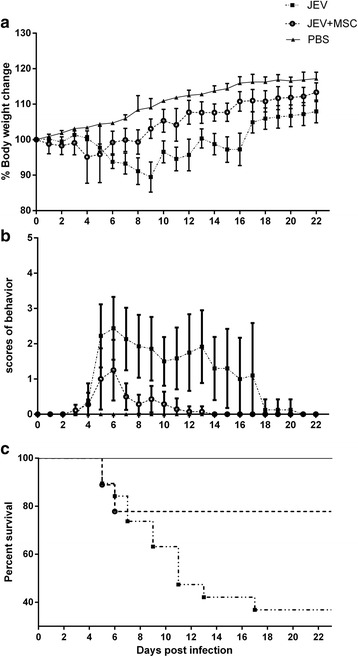
MSC treatment protects mice from JEV infection-induced lethality. Mice were given phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (n = 7) or Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) (n = 36) by intraperitoneal injection. Then, the mice were intravenously injected with either PBS or mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) at 1 and 3 dpi via the tail vein. a The weight of the mice in each group was recorded between 16:30 and 17:00 daily for 22 days until all the groups were completely stable (PBS = 7, JEV = 18, JEV + MSC = 18). b The behavior scores were monitored and recorded twice a day according to the scoring criteria; the data are presented as the mean ± 95% confidence interval (0 = no piloerection, no restriction of movement, no body stiffening, no hind limb paralysis; 1 = piloerection, no restriction of movement, no body stiffening, no hind limb paralysis; 2 = piloerection, restriction of movement, no body stiffening, no hind limb paralysis; 3 = piloerection, restriction of movement, body stiffening, no hind limb paralysis; 4 = piloerection, restriction of movement, body stiffening, hind limb paralysis; 5 = piloerection, restriction of movement, body stiffening, hind limb paralysis, occasional tremor or death. The dead mice were scored as 5 and removed from the cohort). c The death and survival of the mice were recorded every day and then analyzed and presented as Kaplan–Meier survival curves
