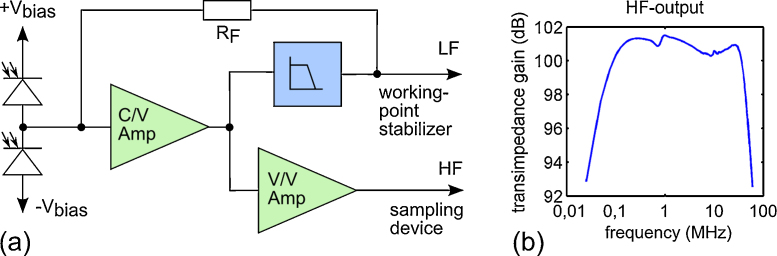
Fig. 3.
(a) Schematic of the in-house designed balanced photodetector. Two reversed-biased photodiodes transform the output of the interferometer into a photocurrent. This current is fed to a transimpedance converter (C/V). A voltage amplifier elevates the output of the C/V stage to a net of 101 dB. A feedback loop, consisting of an active low-pass filter and a resistor (RF), prevents the detector from saturation. A tap of the feedback loop provides the LF-signal, required for the stabilization of the working point. (b) HF-gain measured from 20 kHz to 100 MHz. The −3 dB-points are 54 kHz and 43 MHz.