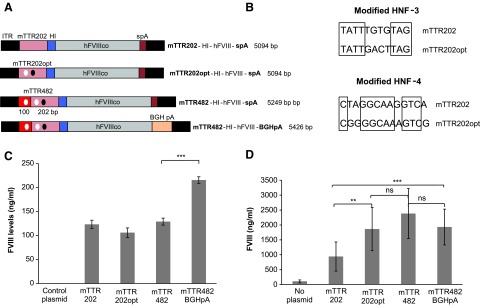
Figure 1.
Characterization of previral plasmids with mouse transthyretin human Factor VIII (mTTR-hFVIII) expression cassettes. (A) Diagram of hFVIII expression cassettes flanked by AAV inverted terminal repeat sequences (ITRs) and with vector genome sizes ranging from 5.1 to 5.4 kb. (B) Sequence modifications in hepatic nuclear factor (HNF)-3 and HNF-4 binding sites. Location of modified binding sites for HNF-3 (black circles) and HNF-4 (white circles) are shown in (A). (C) FVIII levels from mTTR-FVIII expression plasmids in vitro. Previral plasmids were transfected into Huh7 cells, and FVIII protein levels in the culture media were measured 72 h later by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Values were adjusted for transfection efficiency by secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) activity obtained from co-transfected SEAP expressing plasmid. Two independent experiments were performed (n = 3 for each construct) with comparable results. (D) FVIII levels from mTTR-FVIII expression plasmids in vivo. The previral plasmid vectors (30 μg/mouse) were administered by hydrodynamic high-volume injections (2.4 mL/mouse) into the tail veins of C56BL/6 mice (n = 8–10 for plasmid groups; n = 5 for naïve group), and plasma FVIII protein levels were measured by ELISA. Values in each graph represent the average ± standard deviation, and significance was calculated using Student's t-test, with significance indicated as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. Abbreviations: ITR, recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) inverted terminal repeat; mTTR202, mouse core transthyretin promoter (202 bp); mTTR202opt, mTTR with modified HNF-3 and -4 binding sites; mTTR482, mTTR202opt and 100 bp transthyretin enhancer; HI, hybrid intron; hFVIIIco, B-domain deleted human FVIII cDNA; spA, synthetic polyA; BGH, bovine growth hormone; pA, polyA.