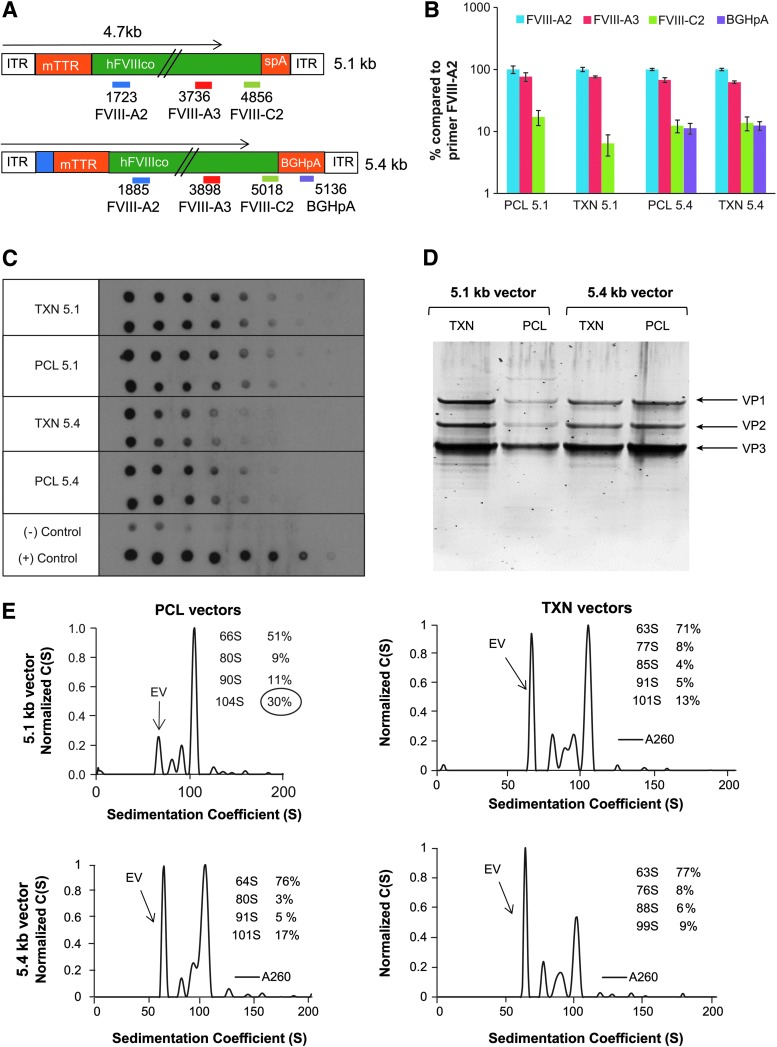
Figure 2.
Characterization of the AAVrh8R/FVIII-5.1 and AAVrh8R/FVIII-5.4 vector preparations. rAAV vectors were generated via producer cell line (PCL; MWs #35 and #163) or transient transfection (TXN) followed by purification via column chromatography. (A) Location of primer/probe sets used to measure titers for 5.1 and 5.4 kb FVIII vector genomes. Primer/probe sets used detect regions located internally (FVIII-A2, FVIII-A3) or toward the terminal ends (outside 4.7 kb from the 3′ terminus; FVIII-C2, BGHpA) of the vector genomes. (B) Vector quantitation with multiple primer/probe sets. The purified vectors used in vivo were titered with multiple primer/probe sets shown in (A). The results are calculated as % of titer compared to the internal primer/probe FVIII-A2 used for most analyses. (C) Evaluation of vector titers by DNA dot blot analysis. Equal amounts of vector genomes (1.5e9 vg) based on quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) with FVIII-A2 primer/probe were loaded in duplicates onto membrane and serially diluted twofold, followed by probing with fragment consisting of the majority of the vector genome (4.7 kb fragment containing promoter and FVIII cDNA). Plasmids containing non-FVIII (negative control) or FVIII (positive control) cDNA were used as controls for signal specificity. (D) Purity of vector lots. Equal amounts of vector (1 × 1010 vg/lane) were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by protein staining with SYPRO stain. The locations of the capsid proteins (VP1, VP2, and VP3) are shown on the right. (E) Quality analysis of vector preparations by analytical ultracentrifugation analysis (AUC). The insert shows the vector sedimentation value (S) and percentage (%) for each peak. The empty virion (EV) peak has an S value of 63–64, while virions with 4.7 kb vector genomes are typically 100S–103S. Additional AAV/FVIII-5.1 lots analyzed by AUC are shown in Supplementary Fig. S3.